Documents
Poster
TCNAS: TRANSFORMER ARCHITECTURE EVOLVING IN CODE CLONE DETECTION
- DOI:
- 10.60864/mnsp-1w65
- Citation Author(s):
- Submitted by:
- Hongyan Xu
- Last updated:
- 6 June 2024 - 10:32am
- Document Type:
- Poster
- Document Year:
- 2024
- Event:
- Presenters:
- Hongyan Xu
- Paper Code:
- MLSP-P28
- Categories:
- Log in to post comments
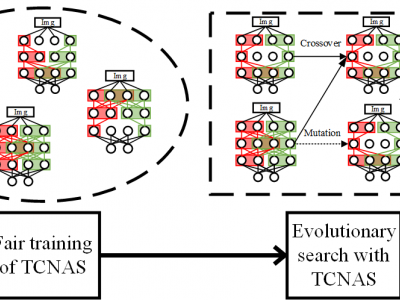
Code clone detection aims at finding code fragments with syntactic or semantic similarity. Most of current approaches mainly focus on detecting syntactic similarity while ignoring semantic long-term context alignment, and these detection methods encode the source code using human-designed models, a process which requires both expert input and a significant cost of time for experimentation and refinement. To address these challenges, we introduce the Transformer Code Neural Architecture Search (TCNAS), an approach designed to optimize transformer-based architectures for detection. In TCNAS, all channels are trained and evaluated equitably to enhance search efficiency. Besides, we introduce the dataflow of the code by extracting the semantic information from the code fragments. TCNAS facilitates the discovery of an optimal model structure geared towards the detection, eliminating the need for manual design. The searched optimal architecture is utilized to detect the code pairs. We conduct various empirical experiments on the benchmark, which covering all four types of code clone detection. The results demonstrate our approach consistently yields competitive detection scores across a range of evaluations.

