
- Read more about Exact Performance of NOMA with Full-Duplex Energy Harvesting Relaying in Nakagami-m Frequency-Selective Fading Channel
- Log in to post comments
GlobalSIP.pdf
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views
- Read more about Obstructed Vehicle-to-Vehicle Channel Modeling for Intelligent Vehicular Communications
- Log in to post comments
In order to realize the vision of intelligent connected vehicles, it is necessary to model the vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) channels in various realistic environments, especially when the line-of-sight (LOS) between transmitter (Tx) and receiver (Rx) is obstructed. In this paper, we model obstructed vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) channels for the 5-GHz band through measurement-validated ray-tracing (RT) simulations. To begin, we establish a realistic V2V RT simulator through integrating three key channel features: small-scale structures (e.g.
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views
- Read more about Experiences in using the Pepper Robotic Platform for Museum Assistance Applicatons
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents the software architecture of a robotic museum guide application called CUMA.
It is intended to run upon the Pepper robotic platform and has the objective of guiding visitors of a museum accompanying them in the tour, explaining museum works, and interacting with them in order to gather feedback.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views
- Read more about Performance of the Asynchronous Consensus Based Bundle Algorithm in Lossy Network Environments
- Log in to post comments
We study multi-agent task allocation where multiple tasks must be divided among multiple autonomous robots. Algorithms
for solving such problems are typically developed under the assumption of perfect communication, without considering
the lossy nature of the underlying wireless network. In this paper, leveraging a sophisticated unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV)
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views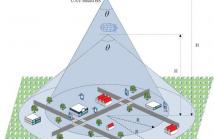
- Read more about The Energy-efficient UAV-based BS Coverage in Air-to-Ground Communications
- Log in to post comments
With the increasing trend of unmanned aerial vehi-cles (UAVs) applications, UAV-based base station (BS) has gained significant popularity for rapid deployable networks. Compared with the fixed infrastructure that could be severally disrupted in the case of natural disasters, the UAV-based BSs are easily for deployment and can provide the emergency communication in the target areas. In addition, for the limited power supply in UAV, energy-efficient transmission is also essential in the wireless coverage. Accordingly, in this paper we focus our attention on
- Categories:
 67 Views
67 Views
- Read more about Cooperative MIMO Precoding with Distributed CSI: A Hierarchical Approach
- Log in to post comments
The problem of network multiple-input multiple-output precoding under distributed channel state information is a notoriously challenging question, for which optimal solutions with reasonable complexity remain elusive. In this context, we assess the value of hierarchical information exchange, whereby an order is established among the transmitters (TXs) in such a way that~a given TX has access not only to its local channel estimate but also to the estimates available at the less informed TXs.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views

- Read more about Estimating message transmission time over heterogeneous chain of disrupted links
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views
- Read more about Optimal Simultaneous Wireless Information and Power Transfer with Low-Complexity Receivers
- Log in to post comments
Nowadays, a significant goal of technology is to prolong the lifetime of the wireless communication devices. To this end, this paper studies and optimizes the performance of simultaneous wireless information and power transfer with an integrated energy and information receiver, which has the advantage of low complexity and energy cost. Specifically, a tractable expression for the achievable rate is provided, which is then used to describe the achievable harvested energy-rate region.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about Multi-Antenna Receiver for Ambient Backscatter Communication Systems
- Log in to post comments
Consider an ambient modulated backscatter communication (AmBC) system adopting binary phase shift keying modulation that the receiver is to decode the backscatter device induced message without knowledge of the channel state information, the statistical channel covariance matrices, and the noise variance at the receiver antennas. In this paper, we apply the fact that the ambient orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) signals with a large number of subcarriers contain repetitive elements inducing time correlation.
SPAWC18.pdf
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views