
Consider a network with N nodes in d dimensions, and M overlapping subsets P_1,...,P_M (subnetworks). Assume that the nodes in a given P_i are observed in a local coordinate system. We wish to register the subnetworks using the knowledge of the observed coordinates. More precisely, we want to compute the positions of the N nodes in a global coordinate system, given P_1,...,P_M and the corresponding local coordinates. Among other applications, this problem arises in divide-and-conquer algorithms for localization of adhoc sensor networks.
- Categories:
 31 Views
31 Views
- Read more about Detection of Pilot-Hopping Sequences for Grant-Free Random Access in Massive MIMO Systems
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 56 Views
56 Views
- Read more about CHANNEL IMPULSIVE NOISE MITIGATION FOR LINEAR VIDEO CODING SCHEMES
- Log in to post comments
The problem of impulse noise mitigation is considered when videos encoded using a SoftCast based Linear Video Coding scheme are transmitted using an OFDM scheme over a wideband channel prone to impulse noise A Fast Bayesian Matching Pursuit algorithm is employed for impulse noise mitigation This approach requires the provisioning of some OFDM subchannels to estimate the impulse noise locations and amplitudes Provisioned subchannels cannot be used to transmit data and lead to a decrease of the nominal decoded video quality at receivers in absence of impulse noise Using a phenomenological mod
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views
- Read more about ON ACHIEVABLE RATES FOR MASSIVE MIMO SYSTEM WITH IMPERFECT CHANNEL COVARIANCE INFORMATION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views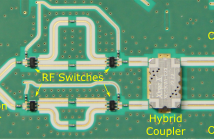
- Read more about Outphasing Elements for Hybrid Analogue Digital Beamforming and Single-RF MIMO
- Log in to post comments
In conventional Multiple-Input Multiple Output (MIMO) systems, each antenna requires its own Radio Frequency (RF) chain. Since each RF-chain includes several active components that have to be synchronised, costs and complexity become restrictive. The outphasing MIMO and the outphasing precoder architectures are possible approaches to mitigate this problem. The core of both architectures are Outphasing Elements (OEs), which are used to form a electronically controllable, passive antenna feed network. These OEs are analysed with respect to component tolerances.
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 Views
- Read more about Hybrid Beamforming: Where Should the Analog Power Amplifiers be Placed?
- Log in to post comments
In this paper we study the spectral efficiency (SE) of a point-to-point massive multiple-input multiple-output system (P2P-massive MIMO) with limited radio frequency (RF) chains, i.e., analog-to-digital/ digital-to-analog (D2A/A2D) modules, at the transceivers. The resulting architecture is known as hybrid beamforming, where the joint analog and digital beamforming optimization maximizes the SE. We analyze the SE of the system by keeping the number of RF-chains low, but placing analog amplifiers at different paths.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views
- Read more about Interference Exploitation Precoding for Multi-Level Modulations
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we investigate the interference exploitation precoding for multi-level modulations in the downlink multi-antenna systems. We mathematically derive the optimal precoding structures based on the Karush-Kuhn-Tucker (KKT) conditions. Furthermore, by formulating the dual problem, the precoding problem for multi-level modulations can be transformed into a pre-scaling operation using quadratic programming (QP) optimization.
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views
- Read more about DISTRIBUTED JOINT TRANSMITTER DESIGN AND SELECTION USING AUGMENTED ADMM
- Log in to post comments
This work considers a design of network in which multiple transmission points (TPs) cooperatively serve users by jointly precoding shared data. Considered problem formulation jointly designs the beamformers and performs TP-UE link selection, which aims in improving overall system rate. Proposed distributed Augmented ADMM algorithm features parallelization among TPs, which has practical importance for computational load distribution and reducing signaling overhead in backhaul.
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views
- Read more about DISTRIBUTED JOINT TRANSMITTER DESIGN AND SELECTION USING AUGMENTED ADMM
- Log in to post comments
This work considers a design of network in which multiple transmission points (TPs) cooperatively serve users by jointly precoding shared data. Considered problem formulation jointly designs the beamformers and performs TP-UE link selection, which aims in improving overall system rate. Proposed distributed Augmented ADMM algorithm features parallelization among TPs, which has practical importance for computational load distribution and reducing signaling overhead in backhaul. This approach is different from others
- Categories:
 35 Views
35 Views
- Read more about Security in the Internet of Things: Information Theoretic Insights
- Log in to post comments
The emerging Internet of Things (IoT) has several salient characteristics that differentiate it from existing wireless networking architectures. These include the deployment of very large numbers of (possibly) low-complexity terminals; the need for low-latency, short-packet communications (e.g., to support automation); light or no infrastructure; and primary applications of data gathering, inference and control.
- Categories:
 43 Views
43 Views