
ICASSP is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The 2019 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.

- Read more about Permissible support patterns for identifying the spreading function of time-varying channels
- Log in to post comments
We study support patterns for covariance matrices that appear in the problem of stochastic time-varying channel identification.
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views
- Read more about Tone Reservation and Solvability Concepts for the PAPR Problem in General Orthonormal Transmission Systems
- Log in to post comments
Large peak to average power ratios (PAPRs) are problematic for communication systems. One possible approach to control the PAPR is the tone reservation method. We analyze the tone reservation method for general complete orthonormal systems, and consider two solvability concepts: strong solvability and weak solvability. Strong solvability requires a rather strong control of the peak value of the transmit signal by the energy of the information signal, and thus might be to restrictive for practical applications.
- Categories:
 76 Views
76 Views
- Read more about On the Computability of System Approximations under Causality Constraints
- Log in to post comments
Approximating the transfer function of stable causal linear systems by a basis expansion is a common task in signal- and system theory. This paper characterizes a scale of signal spaces, containing stable causal transfer functions, with a very simple basis (the Fourier basis) but which is not computable. Thus it is not possible to determine the coefficients of this basis expansion on any digital computer such that the approximation converges to the desired function.
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views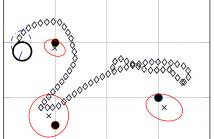
- Read more about Potential-field-based active exploration for acoustic simultaneous localization and mapping
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents a novel framework for active exploration in the context of acoustic \gls{SLAM} using a microphone array mounted on a mobile robotic agent. Acoustic \gls{SLAM} aims at building a map of acoustic sources present in the environment and simultaneously estimating the agent's own trajectory and position within this map. Two important aspects of this task are robustness against disturbances arising from reverberation and sensor imperfections and an appropriate degree of exploration to achieve high map accuracy.
slides.pdf
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about Passive online geometry calibration of acoustic sensor networks
- Log in to post comments
As we are surrounded by an increased number of mobile devices equipped with wireless links and multiple microphones, e.g., smartphones, tablets, laptops and hearing aids, using them collaboratively for acoustic processing is a promising platform for emerging applications.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about DEREVERBERATION AND BEAMFORMING IN FAR-FIELD SPEAKER RECOGNITION
- Log in to post comments
This paper deals with far-field speaker recognition. On a corpus of NIST SRE 2010 data retransmitted in a real room with multiple microphones, we first demonstrate how room acoustics cause significant degradation of state-of-the-art i-vector based speaker recognition system. We then investigate several techniques to improve the performances ranging from probabilistic linear discriminant analysis (PLDA) re-training, through dereverberation, to beamforming.
- Categories:
 51 Views
51 Views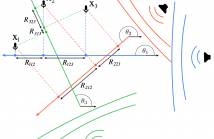
- Read more about Structure from sound with incomplete data
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we consider the problem of jointly localizing a microphone array and identifying the direction of arrival of acoustic events. Under the assumption that the sources are in the far field, this problem can be formulated as a constrained low-rank matrix factorization with an unknown column offset. Our focus is on handling missing entries, particularly when the measurement matrix does not contain a single complete column. This case has not received attention in the literature and is not handled by existing algorithms, however it is prevalent in practice.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views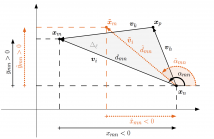
Self-localization of nodes in a sensor network is typically achieved using either range or direction measurements; in this paper, we show that a constructive combination of both improves the estimation. We propose two localization algorithms that make use of the differences between the sensors’ coordinates, or edge vectors; these can be calculated from measured distances and angles. Our first method improves the existing edge-multidimensional scaling algorithm (E-MDS) by introducing additional constraints
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about DATA-AIDED FAST BEAMFORMING SELECTION FOR 5G
- Log in to post comments
Millimeter wave frequencies paired up with MIMO antennas
employing beamforming are seen as critical enablers of next gen-
eration networks. However, selecting the most beneficial beamform-
ing weights in a codebook-enabled downlink transmitter is a lengthy
task, as the existing methods rely on some form of channel mea-
surement. In fact, if the used codebook is too large, the traditional
methods might fail to select an appropriate entry within the channel
coherence time.
In this paper, a new method to assist the beam selection is pro-
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views