
The International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), sponsored by the IEEE Signal Processing Society, is the premier forum for the presentation of technological advances and research results in the fields of theoretical, experimental, and applied image and video processing. ICIP has been held annually since 1994, brings together leading engineers and scientists in image and video processing from around the world. Visit website.

- Read more about Immersive Optical-See-Through Augmented Reality (Keynote Talk)
- Log in to post comments
Immersive Optical-See-Through Augmented Reality. Augmented Reality has been getting ready for the last 20 years, and is finally becoming real, powered by progress in enabling technologies such as graphics, vision, sensors, and displays. In this talk I’ll provide a personal retrospective on my journey, working on all those enablers, getting ready for the coming AR revolution. At Meta, we are working on immersive optical-see-through AR headset, as well as the full software stack. We’ll discuss the differences of optical vs.
- Categories:
 145 Views
145 Views
- Read more about Sparse Modeling
- Log in to post comments
Sparse Modeling in Image Processing and Deep LearningSparse approximation is a well-established theory, with a profound impact on the fields of signal and image processing. In this talk we start by presenting this model and its features, and then turn to describe two special cases of it – the convolutional sparse coding (CSC) and its multi-layered version (ML-CSC). Amazingly, as we will carefully show, ML-CSC provides a solid theoretical foundation to … deep-learning.
- Categories:
 123 Views
123 Views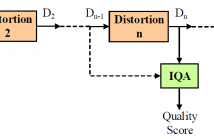
- Read more about Quality Assessment of Images Undergoing Multiple Distortion Stages
- Log in to post comments
In practical media distribution systems, visual content often undergoes multiple stages of quality degradations along the delivery chain between the source and destination. By contrast, current image quality assessment (IQA) models are typically validated on image databases with a single distortion stage. In this work, we construct two large-scale image databases that are composed of more than 2 million images undergoing multiple stages of distortions and examine how state-of-the-art IQA algorithms behave over distortion stages.
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views
- Read more about Automatic Generation of Epipolar Curves
- Log in to post comments
Fisheye camera is widely used in various applications because of its wider field-of-view. However, high distortion of images captured by fisheye cameras make it difficult for certain tasks which are based on traditional epipolar geometry (using epipolar lines) and stereo correspondence, such as depth map estimation. While most of existing depth map estimation methods use perspective-projection-based camera model, considering fisheye camera for depth map estimation will be beneficial because of its wider FOV.
- Categories:
 70 Views
70 Views
- Read more about Sparse Modeling in Image Processing and Deep Learning (Keynote Talk)
- Log in to post comments
Sparse approximation is a well-established theory, with a profound impact on the fields of signal and image processing. In this talk we start by presenting this model and its features, and then turn to describe two special cases of it – the convolutional sparse coding (CSC) and its multi-layered version (ML-CSC). Amazingly, as we will carefully show, ML-CSC provides a solid theoretical foundation to … deep-learning.
- Categories:
 348 Views
348 Views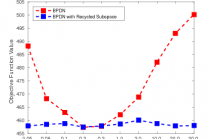
- Read more about ADMM Penalty Parameter Selection with Krylov Subspace Recycling Technique for Sparse Coding
- Log in to post comments
The alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) has been widely used for a very wide variety of imaging inverse problems. One of the disadvantages of this method, however, is the need to select an algorithm parameter, the penalty parameter, that has a significant effect on the rate of convergence of the algorithm. Although a number of heuristic methods have been proposed, as yet there is no general theory providing a good choice of this parameter for all problems.
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views- Read more about GLAND SEGMENTATION GUIDED BY GLANDULAR STRUCTURES: A LEVEL SET FRAMEWORK WITH TWO LEVELS
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views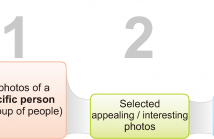
- Read more about Probabilistic Approach to People-Centric Photo Selection and Sequencing
- Log in to post comments
We present a crowdsourcing (CS) study to examine how specific attributes probabilistically affect the selection and sequencing of images from personal photo collections. 13 image attributes are explored, including 7 people-centric properties. We first propose a novel dataset shaping technique based on Mixed Integer Linear Programming (MILP) to identify a subset of photos in which the attributes of interest are uniformly distributed and minimally correlated.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views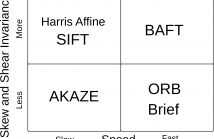
- Read more about BAFT: Binary Affine Feature Transform
- Log in to post comments
We introduce BAFT, a fast binary and quasi affine invariant local image feature. It combines the affine invariance of Harris Affine feature descriptors with the speed of binary descriptors such as BRISK and ORB. BAFT derives its speed and precision from sampling local image patches in a pattern that depends on the second moment matrix of the same image patch. This approach results in a fast but discriminative descriptor, especially for image pairs with large perspective changes.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views- Read more about HIGHLY PARALLEL HEVC MOTION ESTIMATION BASED ON MULTIPLE TEMPORAL PREDICTORS AND NESTED DIAMOND SEARCH
- 3 comments
- Log in to post comments
Rate-constrained motion estimation (RCME) is the most computationally intensive task of H.265/HEVC encoding. Massively parallel architectures, such as graphics processing units (GPUs), used in combination with a multi-core central processing unit (CPU), provide a promising computing platform to achieve fast encoding. However, the dependencies in deriving motion vector predictors (MVPs) prevent the parallelization of prediction units (PUs) processing at a frame level.
- Categories:
 42 Views
42 Views