
The International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), sponsored by the IEEE Signal Processing Society, is the premier forum for the presentation of technological advances and research results in the fields of theoretical, experimental, and applied image and video processing. ICIP has been held annually since 1994, brings together leading engineers and scientists in image and video processing from around the world. Visit website.
- Read more about DenseNet for Dense Flow
- Log in to post comments
Classical approaches for estimating optical flow have achieved rapid progress in the last decade. However, most of them are too slow to be applied in real-time video analysis. Due to the great success of deep learning, recent work has focused on using CNNs to solve such dense prediction problems. In this paper, we investigate a new deep architecture, Densely Connected Convolutional Networks (DenseNet), to learn optical flow. This specific architecture is ideal for the problem at hand as it provides shortcut connections throughout the network, which leads to implicit deep supervision.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views- Read more about Greedy Deep Transform Learning
- Log in to post comments
We introduce deep transform learning – a new
tool for deep learning. Deeper representation is learnt by
stacking one transform after another. The learning proceeds in
a greedy way. The first layer learns the transform and features
from the input training samples. Subsequent layers use the
features (after activation) from the previous layers as training
input. Experiments have been carried out with other deep
representation learning tools – deep dictionary learning,
stacked denoising autoencoder, deep belief network and PCANet
- Categories:
 73 Views
73 Views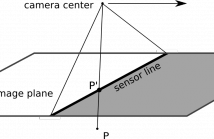
- Read more about Robust Plane-based Calibration for linear cameras
- Log in to post comments
A linear, or 1D, camera is a type of camera that sweeps a linear sensor array over the scene, rather than capturing the scene using a single impression on a 2D sensor array.
They are often used in satellite imagery, industrial inspection, or hyperspectral imaging.
In satellite imaging calibration is often done through a collection of ground points for which the 3D locations are known.
In other applications, e.g. hyperspectral imaging, such known points are not available and annotating many different points is onerous.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 ViewsLarge scale images allow pathologists to perform reviews, using
computer workstations instead of microscopes. This trend raises
a wide range of issues related to the management of these massive
datasets. In particular, efficient solutions for data storage and processing
have to be developed in order to deliver increasingly reliable
and faster analyses. In addition, the improvement of workflows also
requires the reinforcement of visualization capabilities. In this paper,
we present a new virtual microscopy (VM) approach for interactivetime
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views- Read more about IMAGE SEGMENTATION USING CONTOUR, SURFACE, AND DEPTH CUES (Slides)
- Log in to post comments
We target at solving the problem of automatic image segmentation. Although 1D contour and 2D surface cues have been widely utilized in existing work, 3D depth information of an image, a necessary cue according to human visual perception, is however overlooked in automatic image segmentation. In this paper, we study how to fully utilize 1D contour, 2D surface, and 3D depth cues for image segmentation. First, three elementary segmentation modules are developed for these cues respectively.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views- Read more about IMAGE SEGMENTATION USING CONTOUR, SURFACE, AND DEPTH CUES (Poster)
- Log in to post comments
We target at solving the problem of automatic image segmentation. Although 1D contour and 2D surface cues have been widely utilized in existing work, 3D depth information of an image, a necessary cue according to human visual perception, is however overlooked in automatic image segmentation. In this paper, we study how to fully utilize 1D contour, 2D surface, and 3D depth cues for image segmentation. First, three elementary segmentation modules are developed for these cues respectively.
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views- Read more about Supervised Evaluation of the Quality of BinaryPartition Trees based on Uncertain Semantic Ground-Truth for Image Segmentation Purpose
- Log in to post comments
The binary partition tree (BPT) is a hierarchical data-structure that
models the content of an image in a multiscale way. In particular,
a cut of the BPT of an image provides a segmentation, as a partition
of the image support. Actually, building a BPT allows for
dramatically reducing the search space for segmentation purposes,
based on intrinsic (image signal) and extrinsic (construction metric)
information. A large literature has been devoted to the construction
on such metrics, and the associated choice of criteria (spectral, spatial,
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views- Read more about 3D Mesh Coding with Predefined Region-of-Interest
- Log in to post comments
We introduce a novel functionality for wavelet-based irregular mesh codecs which allows for prioritizing at the encoding side a region-of-interest (ROI) over a background (BG), and for transmitting the encoded data such that the quality in these regions increases first. This is made possible by appropriately scaling wavelet coefficients. To improve the decoded geometry in the BG, we propose an ROI-aware inverse wavelet transform which only upscales the connectivity in the required regions. Results show clear bitrate and vertex savings.
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views- Read more about Intelligent Detail Enhancement for Differently Exposed Images
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views- Read more about DEEP LEARNING ARCHITECTURE FOR PEDESTRIAN 3-D LOCALIZATION AND TRACKING USING MULTIPLE CAMERAS
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views