
The International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), sponsored by the IEEE Signal Processing Society, is the premier forum for the presentation of technological advances and research results in the fields of theoretical, experimental, and applied image and video processing. ICIP has been held annually since 1994, brings together leading engineers and scientists in image and video processing from around the world. Visit website.
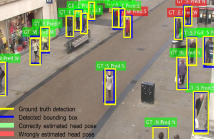
- Read more about Tiny Head Pose Classification by Bodily Cues
- Log in to post comments
The head pose is an important cue for computer vision. Traditionally considered in human computer interaction applications,
it becomes very hard to model in surveillance scenarios, due to the tiny head size. Additionally, no public dataset contains continuous head pose annotations in open scenery, making the challenge even harder to face. Here we present a
framework based on Faster RCNN, which introduces a branch in the network architecture related to the head pose estimation.
- Categories:
 235 Views
235 Views- Read more about MULTI-VIEW NETWORK-BASED SOCIAL-TAGGED LANDMARK IMAGE CLUSTERING
- Log in to post comments
The multiple types of social media data have abundant information, but learning multi-modal social data is challenging due to data heterogeneity and noise in user-generated data. To address this problem, we propose a multi-view network-based clustering approach that is robust to noise and fully reflects the underlying structure of the comprehensive network. To demonstrate the proposed approach, we experimented with clustering challenging tagged images of landmarks.
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views- Read more about INTEGRATING THOR TOOLS INTO THE EMERGING AV1 CODEC
- Log in to post comments
Over recent years there have been several efforts which aim to standardise a royalty-free video codec, such as Thor developed by Cisco, and AV1 developed by the Alliance for Open Media. In this paper we discuss how some compression tools in Thor were integrated into the emerging AV1 codec aiming to increase compression efficiency as well as to decrease computational complexity.
- Categories:
 101 Views
101 Views
Eyes represent the most distinctive features of the human face, while their position and movements are a significant source of information about the cognitive and affective state of humans. Precise eye center localization constitutes a challenging problem in many human-computer interaction applications. In this work, an automatic, non-intrusive method is introduced for the precise eye center localization,based on a modified version of the Fast Radial Symmetry Transform.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 ViewsIn recent years, the triplet loss-based deep neural networks (DNN) are widely used in the task of face recognition and achieve the state-of-the-art performance. However, the complexity of training the triplet loss-based DNN is significantly high due to the difficulty in generating high-quality training samples. In this paper, we propose a novel DNN training framework to accelerate the training process of the triplet loss-based DNN and meanwhile to improve the performance of face recognition. More specifically, the proposed framework contains two stages: 1) The DNN initialization.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views- Read more about GPGPU Implementation of VP9 in-loop deblocking filter and improvement for AV1 codec
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 110 Views
110 Views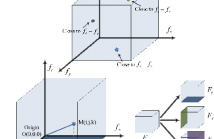
- Read more about Saliency Detection for Seismic Applications Using Multi-dimensional Spectral Projections and Directional Comparisons
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose a novel approach for saliency detection for seismic applications using 3D-FFT local spectra and multi-dimensional plane projections. We develop a projection scheme by dividing a 3D-FFT local spectrum of a data volume into three distinct components, each depicting changes along a different dimension of the data. The saliency detection results obtained using each projected component are then combined to yield a saliency map.
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views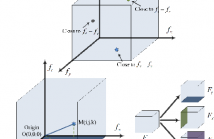
- Read more about Saliency Detection for Seismic Applications Using Multi-dimensional Spectral Projections and Directional Comparisons
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose a novel approach for saliency detection for seismic applications using 3D-FFT local spectra and multi-dimensional plane projections. We develop a projection scheme by dividing a 3D-FFT local spectrum of a data volume into three distinct components, each depicting changes along a different dimension of the data. The saliency detection results obtained using each projected component are then combined to yield a saliency map.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about UNSUPERVISED FEATURE SELECTION BY MANIFOLD REGULARIZED SELF-REPRESENTATION
- Log in to post comments
Unsupervised feature selection has been proven to be an efficient technique in mitigating the curse of dimensionality. It helps to understand and analyze the prevalent high-dimensional unlabeled data. Recently, based on the self-similarity property of objects, self-representation which assumes that a feature can be represented by the linear combination of its relevant features has been successfully used in unsupervised feature selection. In this paper, we propose a novel algorithm termed Manifold Regularized Selfrepresentation(MRSR) based on the self-representation ability of features.
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 ViewsFully connected multi layer neural networks such as Deep Boltzmann Machines (DBM) performs better than fully connected single layer neural networks in image classification tasks and has a smaller number of hidden layer neurons than Extreme Learning Machine (ELM) based fully connected multi layer neural networks such as Multi Layer ELM (ML-ELM) and Hierarchical ELM (H-ELM) However, ML-ELM and H-ELM has a smaller training time than DBM.
- Categories:
 46 Views
46 Views