
The International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), sponsored by the IEEE Signal Processing Society, is the premier forum for the presentation of technological advances and research results in the fields of theoretical, experimental, and applied image and video processing. ICIP has been held annually since 1994, brings together leading engineers and scientists in image and video processing from around the world. Visit website.
In the past five years, salient object detection has become one of the hot topics in the field of computer vision. Focus is a naturally strong indicator for the salient object detection task, but is not well studied. A novel method is proposed in this paper to estimate the focus prior map for an arbitrary image. Different from the current edge density estimation based methods, the proposed method is based on the sparse defocus dictionary learning at a newly designed dataset. The focus strength is measured by the number of non-zero coefficients of the dictionary atoms.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views- Read more about FACIAL EXPRESSION RECOGNITION USING SVM CLASSIFICATION ON MIC-MACRO PATTERNS
- Log in to post comments
Real-time identification of facial expressions is an important topic in the area of human computer interaction and pattern recognition. The research has gained significant attention in recent years. However, many challenges still exist. This is because an individual might display different expressions at different times even for the same mood. Expressions can also be influenced by health. Our proposed framework aims to capture unique information related to facial expressions from salient patches.
- Categories:
 51 Views
51 Views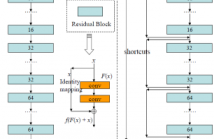
- Read more about Residual Networks of Residual Networks: Multilevel Residual Networks
- Log in to post comments
A residual-networks family with hundreds or even thousands of layers dominates major image recognition tasks, but building a network by simply stacking residual blocks inevitably limits its optimization ability. This paper proposes a novel residual-network architecture, Residual networks of Residual networks (RoR), to dig the optimization ability of residual networks. RoR substitutes optimizing residual mapping of residual mapping for optimizing original residual mapping.
ICIP 2017.pdf
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views- Read more about Age Group Classification in the Wild with Deep RoR Architecture
- Log in to post comments
Automatically predicting age group from face images acquired in unconstrained conditions is an important and challenging task in many real-world applications. Nevertheless, the conventional methods with manually-designed features on in-the-wild benchmarks are unsatisfactory because of incompetency to tackle large variations in unconstrained images.
- Categories:
 61 Views
61 Views- Read more about FACIAL ANALYSIS IN THE WILD WITH LSTM NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 2 Views
2 Views- Read more about FACIAL ANALYSIS IN THE WILD WITH LSTM NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views
- Read more about Dictionary Learning-based Image Compression
- Log in to post comments
Dictionary learning based image compression has attracted a lot of research efforts due to the inherent sparsity of image contents. Most algorithms in the literature, however, suffer from two drawbacks. First, the atoms selected for image patch reconstruction scatter over the entire dictionary, which leads to a high coding cost. Second, the sparse representation of image patches is performed independently from the quantization of sparse coefficients, which may result in a sub-optimal solution.
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views- Read more about CODING BLOCK-LEVEL PERCEPTUAL VIDEO CODING FOR 4:4:4 DATA IN HEVC
- Log in to post comments
There is an increasing consumer demand for high bit-depth 4:4:4 HD video data playback due to its superior perceptual visual quality compared with standard 8-bit subsampled 4:2:0 video data. Due to vast file sizes and associated bitrates, it is desirable to compress raw high bit-depth 4:4:4 HD video sequences as much as possible without incurring a discernible decrease in visual quality. In this paper, we propose a Coding Block (CB)-level perceptual video coding technique for HEVC named Full Color Perceptual Quantization (FCPQ).
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views- Read more about POINT DENSITY-INVARIANT 3D OBJECT DETECTION AND POSE ESTIMATION
- Log in to post comments
For 3D object detection and pose estimation, it is crucial to extract distinctive and representative features of the objects and describe them efficiently. Therefore, a large number of 3D feature descriptors has been developed. Among these, Point Feature Histogram RGB (PFHRGB) has been evaluated as showing the best performance for 3D object and category recognition. However, this descriptor is vulnerable to point density variation and produces many false correspondences accordingly.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 ViewsCurrent object segmentation algorithms are based on the hypothesis that one has access to a very large amount of data. In this paper, we aim to segment objects using only tiny datasets. To this extent, we propose a new automatic part-based object segmentation algorithm for non-deformable and semi-deformable objects in natural backgrounds. We have developed a novel shape descriptor which models the local boundaries of an object's part. This shape descriptor is used in a bag-of-words approach for object detection.
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views