
The International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), sponsored by the IEEE Signal Processing Society, is the premier forum for the presentation of technological advances and research results in the fields of theoretical, experimental, and applied image and video processing. ICIP has been held annually since 1994, brings together leading engineers and scientists in image and video processing from around the world. Visit website.
- Read more about Learning a Cross-Modal Hashing Network for Multimedia Search
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose a cross-modal hashing network (CMHN) method to learn compact binary codes for cross-modality multimedia search. Unlike most existing cross-modal hashing methods which learn a single pair of projections to map each example into a binary vector, we design a deep neural network to learn multiple pairs of hierarchical non-linear transformations, under which the nonlinear characteristics of samples can be well exploited and the modality gap is well reduced.
- Categories:
 49 Views
49 Views- Read more about Joint Tracking and Gait Recognition of Multiple People in Video
- Log in to post comments
We propose a novel approach to address the problem of jointly tracking and gait recognition of multiple people in a video sequence. The most state of the art algorithms for gait recognition consider the cases where there is only one person without any occlusion in a very constrained environment. However, in real scenarios such as in airports, train stations, etc, there are many people in the environment that make these algorithms inapplicable.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views- Read more about 2563 sliding window filter based unknown object pose estimation
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views- Read more about Correlation Model Selection for interactive video communication
- Log in to post comments
Interactive video communication has been recently proposed for multi-view videos. In this scheme, the server has to store the views as compact as possible, while being able to transmit them independently to the users, who are allowed to navigate interactively among the views, hence requesting a subset of them. To achieve this goal, the compression must be done using a model-based coding in which the correlation between the predicted view generated on the user side and the original view has to be modeled by a statistical distribution.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views- Read more about Granularity-Based Interactive Image Display
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents a prototype system that assists users in accessing an unstructured image set (e.g., search results of a query). The system provides a spectrum of overviews, each of which is determined by the display granularity (i.e., the level of summary) an user desires. This new functionality enables a new granularity-based interactive image browsing experience.
- Categories:
 223 Views
223 Views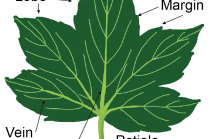
We introduce a new reference axis for leaf classification. The new reference axis, called a Mid-Leaf axis, is based on a quadratic curve that lies on the middle of a leaf. This curve is derived from three basic landmark points: an apex, a centroid, and a petiole. After mapping to a new plane based on this curve, leaf shape features are invariant under translation, rotation, scaling, and bending. We propose the leaf shape features based on partitioning the morphological features and the tangent’s direction angle of the leaf contour.
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views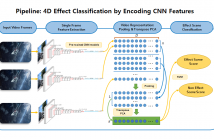
- Read more about 4D Effect Classification by Encoding CNN Features
- Log in to post comments
4D effects are physical effects simulated in sync with videos, movies, and games to augment the events occurring in a story or a virtual world. Types of 4D effects commonly used for the immersive media may include seat motion, vibration, flash, wind, water, scent, thunderstorm, snow, and fog. Currently, the recognition of physical effects from a video is mainly conducted by human experts. Although 4D effects are promising in giving immersive experience and entertainment, this manual production has been the main obstacle to faster and wider application of 4D effects.
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 ViewsSegmenting microvascular structures is an important requirement in understanding angioadaptation by which vascular networks remodel their morphological structures. Accurate segmentation for separating microvasculature structures is important in quantifying remodeling process. In this work, we utilize a deep convolutional neural network (CNN) framework for obtaining robust segmentations of microvasculature from epifluorescence microscopy imagery of mice dura mater.
- Categories:
 60 Views
60 Views- Read more about SAR Image Despeckling by Combination of Fractional-Order Total Variation and Nonlocal Low Rank Regularization
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes a combinational regularization model for synthetic aperture radar (SAR) image despeckling. In contrast to most of the well-known regularization methods that only use one image prior property, the proposed combinational regularization model includes both fractional-order total variation (FrTV) regularization term and nonlocal low rank (NLR) regularization term.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views- Read more about Integrated Deep and Shallow Networks for Salient Object Detection
- Log in to post comments
icip-ppt.pdf
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views