
- Read more about Channel Estimation in Underdetermined Systems Utilizing Variational Autoencoders
- Log in to post comments
In this work, we propose to utilize a variational autoencoder (VAE) for channel estimation (CE) in underdetermined (UD) systems. The basis of the method forms a recently proposed concept in which a VAE is trained on channel state information (CSI) data and used to parameterize an approximation to the mean squared error (MSE)-optimal estimator. The contributions in this work extend the existing framework from fully-determined (FD) to UD systems, which are of high practical relevance.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views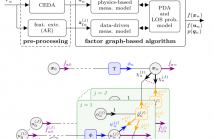
- Read more about A Neural-enhanced Factor Graph-based Algorithm for Robust Positioning in Obstructed LOS Situations
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents a neural-enhanced probabilistic model and corresponding factor graph-based sum-product algorithm for robust localization and tracking in multipath-prone environments. The introduced hybrid probabilistic model consists of physics-based and data-driven measurement models capturing the information contained in both, the line-of-sight (LOS) component as well as in multipath components (NLOS components).
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views
- Read more about Bayesian Tensor Tucker Completion With A Flexible Core
- 2 comments
- Log in to post comments
Tensor completion is a vital task in multi-dimensional signal processing and machine learning. To recover the missing data in a tensor, various low-rank structures of a tensor can be assumed, and Tucker format is a popular choice. However, the promising capability of Tucker completion is realized only when we can determine a suitable multilinear rank, which controls the model complexity and thus is essential to avoid overfitting/underfitting.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
Tensor completion is a vital task in multi-dimensional signal processing and machine learning. To recover the missing data in a tensor, various low-rank structures of a tensor can be assumed, and Tucker format is a popular choice. However, the promising capability of Tucker completion is realized only when we can determine a suitable multilinear rank, which controls the model complexity and thus is essential to avoid overfitting/underfitting.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views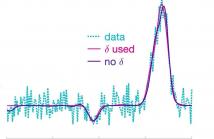
- Read more about Poster: Reversible Jump Markov chain Monte Carlo for Pulse Fitting
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes a reversible jump Markov chain Monte Carlo method that provides efficient inference for the general problem of pulse fitting. In particular, it minimises the potential of an adopted parametric model overfitting to the (noisy) data via the inclusion of a peak proximity parameter. This facilitates learning a more representative underlying model and significantly reduces the computational cost. Synthetic and real data are used to demonstrate the efficacy of the introduced Bayesian technique.
Contact: afg30@cam.ac.uk
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views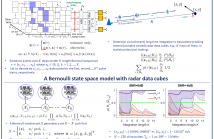
- Read more about Coherent long-time integration and Bayesian detection with Bernoulli track-before-detect
- Log in to post comments
We consider the problem of detecting small and manoeuvring objects with staring array radars. Coherent processing and long-time integration are key to addressing the undesirably low signal-to-noise/background conditions in this scenario and are complicated by the object manoeuvres. We propose a Bayesian solution that builds upon a Bernoulli state space model equipped with the likelihood of the radar data cubes through the radar ambiguity function. Likelihood evaluation in this model corresponds to coherent long-time integration.
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views
- Read more about Alternating Constrained Minimization based Approximate Message Passing
- Log in to post comments
Generalized Approximate Message Passing (GAMP) allows for Bayesian inference in linear models with non-identically independently distributed (n.i.i.d.) priors and n.i.i.d. measurements of the linear mixture outputs. It represents an efficient technique for approximate inference, which becomes accurate when both rows and columns of the measurement matrix can be treated as sets of independent vectors and both dimensions become large.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about High-Dimensional Sparse Bayesian Learning without Covariance Matrices
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about Adaptive Group Testing with Mismatched Models
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about PremiUm-CNN: Propagating Uncertainty Towards Robust Convolutional Neural Networks
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 44 Views
44 Views