- Read more about Energy Efficient Wake-Up Solution For Largescale Internet Of Underwater Things Networks
- Log in to post comments
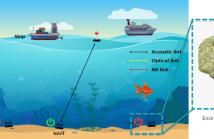
Underwater monitoring and exploration have enhanced significantly due to the wide adoption of Internet of Underwater Things (IoUT). However, IoUT implementation is limited by batteries that require frequent replacement, which is costly and unfeasible due to the hostile aquatic environment. Therefore, it is crucial to implement an energy-efficient solution that maximizes the lifetime of IoUT devices, and hence reduce the overall cost of the system.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views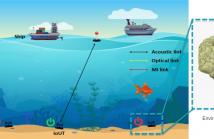
- Read more about Energy Efficient Wake-Up Solution For Largescale Internet Of Underwater Things Networks
- Log in to post comments
Underwater monitoring and exploration have enhanced significantly due to the wide adoption of Internet of Underwater Things (IoUT). However, IoUT implementation is limited by batteries that require frequent replacement, which is costly and unfeasible due to the hostile aquatic environment. Therefore, it is crucial to implement an energy-efficient solution that maximizes the lifetime of IoUT devices, and hence reduce the overall cost of the system.
- Categories:
 31 Views
31 Views
- Read more about State-Augmented Information Routing in Communication Systems with Graph Neural Networks
- Log in to post comments
We consider the problem of routing network packets in a large-scale communication system where the nodes have access to only local information. We formulate this problem as a constrained learning problem, which can be solved using a distributed optimization algorithm. We approach this distributed optimization using a novel state-augmentation (SA) strategy to maximize the aggregate information packets at different source nodes, leveraging dual variables corresponding to flow constraint violations.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views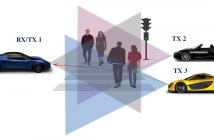
- Read more about Space-Time Adaptive Processing for radars in Connected and Automated Vehicular Platoons
- Log in to post comments
In this study, we develop a holistic framework for space-time adaptive processing (STAP) in connected and automated vehicle (CAV) radar systems. We investigate a CAV system consisting of multiple vehicles that transmit frequency-modulated continuous-waveforms (FMCW), thereby functioning as a multistatic radar. Direct application of STAP in a network of radar systems such as in a CAV may lead to excess interference. We exploit time division multiplexing (TDM) to perform transmitter scheduling over FMCW pulses to achieve high detection performance.
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
- Read more about UAV OPERATION TIME MINIMIZATION FOR WIRELESS-POWERED DATA COLLECTION
- Log in to post comments
Employing unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) for data collection is crucial in facilitating autonomous monitoring applications within wireless sensor networks (WSNs). To enable sustainable WSNs, wireless powering of ground nodes (GNs) from a flying UAV is a promising technique. However, to maximize utility, we need to smartly allocate the limited resources of UAVs. To this end, we propose jointly optimizing the UAV’s trajectory and time allocation per GN to reduce operation time.
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about Secure Energy Efficiency Fairness Maximization in Backscatter Throughput Constrained UAV-assisted Data Collection
- Log in to post comments
Collecting reliable data over extended areas in rural environments for surveillance purposes requires low-cost and effective technologies. This paper proposes a backscattering data collection system that uses unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) to overcome wireless coverage challenges in rural areas. The proposed system provides physical layer security during autonomous data collection, and we optimize the UAV’s trajectory to manage data leakage while taking into account the limited battery of the UAV.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about Debris sensing based on LEO constellation: an intersatellite channel parameter estimation approach
- Log in to post comments
Space debris detection and tracking, a key enabler for Space Situational Awareness (SSA), poses two inherent challenges: (1) small-sized targets (e.g., $1-10~cm$) posing detection difficulties for conventional ground-based radars (GBRs) and optical measurements; (2) large number resulting in a costly tracking exercise. To address these, this work utilizes intersatellite link (ISL) in the emerging low earth orbit (LEO) constellations to opportunistically sense debris. The spatially dense-distributed debris is modeled as a cluster to reduce the number of quantities estimated.
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views
- Read more about SCALING RESULTS FOR ROBUST DISTRIBUTED ESTIMATION IN SENSOR NETWORKS USING ORDER STATISTICS
- Log in to post comments
Robust modeling of estimation error in a distributed sensor
network under random sensing environment is a challenging problem. In this paper, we propose a novel methodology
based on order statistics to statistically model scaling behavior of the mean-squared error (MSE) for distributed estimation in a wireless sensor network. In particular, by leveraging
order statistics of the random signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs)
over the entire network, we derive and compute cumulative
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views
- Read more about Reducing the Communication and Computational Cost of Random Fourier Features Kernel LMS in Diffusion Networks
- Log in to post comments
Diffusion kernel algorithms are interesting tools for distributed nonlinear estimation. However, for the sake of feasibility, it is essential in practice to restrict their computational cost and the number of communications. In this paper, we propose a censoring algorithm for adaptive kernel diffusion networks based on random Fourier features that locally adapts the number of nodes censored according to the estimation error.
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about Delay-aware Backpressure Routing Using Graph Neural Networks
- Log in to post comments
We propose a throughput-optimal biased backpressure (BP) algorithm for routing, where the bias is learned through a graph neural network that seeks to minimize end-to-end delay. Classical BP routing provides a simple yet powerful distributed solution for resource allocation in wireless multi-hop networks but has poor delay performance. A low-cost approach to improve this delay performance is to favor shorter paths by incorporating pre-defined biases in the BP computation, such as a bias based on the shortest path (hop) distance to the destination.
- Categories:
 54 Views
54 Views