
The problem of maximizing the information flow through a sensor network tasked with an inference objective at the fusion center is considered. The sensor nodes take observations, compress, and send them to the fusion center through a network of relays. The network imposes capacity constraints on the rate of transmission in each connection and flow conservation constraints. It is shown that this rate-constrained inference problem can be cast as a Network Utility Maximization problem by suitably defining the utility functions for each sensor, and can be solved using existing techniques.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
Automobiles have become an essential part of everyday lives. In this work, we attempt to make them smarter by introducing the idea of in-car driver authentication using wireless sensing. Our aim is to develop a model which can recognize drivers automatically. Firstly, we address the problem of "changing in-car environments", where the existing wireless sensing based human identification system fails. To this end, we build the first in-car driver radio biometric dataset to understand the effect of changing environments on human radio biometrics.
- Categories:
 49 Views
49 Views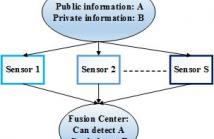
- Read more about MULTILAYER SENSOR NETWORK FOR INFORMATION PRIVACY
- Log in to post comments
A sensor network wishes to transmit information to a fusion center to allow it to detect a public hypothesis, but at the same time prevent it from inferring a private hypothesis. We propose a multilayer sensor network structure, where each sensor first applies a nonlinear fusion function on the information it receives from sensors in a previous layer, and then a linear weighting matrix to distort the information it sends to sensors in the next layer.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views