
- Read more about Summarization of Human Activity Videos Via Low-Rank Approximation
- Log in to post comments
Summarization of videos depicting human activities is a timely problem with important applications, e.g., in the domains of surveillance or film/TV production, that steadily becomes more relevant. Research on video summarization has mainly relied on global clustering or local (frame-by-frame) saliency methods to provide automated algorithmic
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views
- Read more about Summarization of Human Activity Videos Via Low-Rank Approximation
- Log in to post comments
Summarization of videos depicting human activities is a timely problem with important applications, e.g., in the domains of surveillance or film/TV production, that steadily becomes more relevant. Research on video summarization has mainly relied on global clustering or local (frame-by-frame) saliency methods to provide automated algorithmic
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about Fast and Stable Signal Deconvolution via Compressible State-Space Models
- Log in to post comments
Objective: Common biological measurements are in
the form of noisy convolutions of signals of interest with possibly
unknown and transient blurring kernels. Examples include EEG
and calcium imaging data. Thus, signal deconvolution of these
measurements is crucial in understanding the underlying biological
processes. The objective of this paper is to develop fast and
stable solutions for signal deconvolution from noisy, blurred and
undersampled data, where the signals are in the form of discrete
- Categories:
 47 Views
47 Views
- Read more about Rethinking Sketching as Sampling: Efficient Approximate Solution to Linear Inverse Problems
- Log in to post comments
Sampling and reconstruction of bandlimited graph signals have well-appreciated merits for dimensionality reduction, affordable storage, and online processing of streaming network data. However, these parsimonious signals are oftentimes encountered with high-dimensional linear inverse problems. Hence, interest shifts from reconstructing the signal itself towards instead approximating the input to a prescribed linear operator efficiently.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views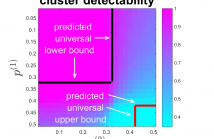
- Read more about Multilayer Spectral Graph Clustering via Convex Layer Aggregation
- Log in to post comments
Multilayer graphs are commonly used for representing different relations between entities and handling heterogeneous data processing tasks. New challenges arise in multilayer graph clustering for assigning clusters to a common multilayer node set and for combining information from each layer. This paper presents a theoretical framework for multilayer spectral graph clustering of the nodes via convex layer aggregation.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about Rethinking Sketching as Sampling: Efficient Approximate Solution to Linear Inverse Problems
- Log in to post comments
Sampling and reconstruction of bandlimited graph signals have well-appreciated merits for dimensionality reduction, affordable storage, and online processing of streaming network data. However, these parsimonious signals are oftentimes encountered with high-dimensional linear inverse problems. Hence, interest shifts from reconstructing the signal itself towards instead approximating the input to a prescribed linear operator efficiently.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about Scalable and Robust PCA Approach with Random Column/Row Sampling
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 2 Views
2 Views
- Read more about Approximate Support Recovery of Atomic Line Spectral Estimation: A Tale of Resolution and Precision
- Log in to post comments
This work investigates the parameter estimation performance of super-resolution line spectral estimation using atomic norm minimization. The focus is on analyzing the algorithm's accuracy of inferring the frequencies and complex magnitudes from noisy observations. When the Signal-to-Noise Ratio is reasonably high and the true frequencies are separated by $O(\frac{1}{n})$, the atomic norm estimator is shown to localize the correct number of frequencies, each within a neighborhood of size $O(\sqrt{\frac{\log n}{n^3}} \sigma)$ of one of the true frequencies.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about Approximate Support Recovery of Atomic Line Spectral Estimation: A Tale of Resolution and Precision
- Log in to post comments
This work investigates the parameter estimation performance of super-resolution line spectral estimation using atomic norm minimization. The focus is on analyzing the algorithm's accuracy of inferring the frequencies and complex magnitudes from noisy observations. When the Signal-to-Noise Ratio is reasonably high and the true frequencies are separated by $O(\frac{1}{n})$, the atomic norm estimator is shown to localize the correct number of frequencies, each within a neighborhood of size $O(\sqrt{\frac{\log n}{n^3}} \sigma)$ of one of the true frequencies.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views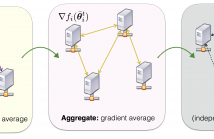
- Read more about A Projection-free Decentralized Algorithm for Non-convex Optimization
- Log in to post comments
This paper considers a decentralized projection free algorithm for non-convex optimization in high dimension. More specifically, we propose a Decentralized Frank-Wolfe (DeFW)
algorithm which is suitable when high dimensional optimization constraints are difficult to handle by conventional projection/proximal-based gradient descent methods. We present conditions under which the DeFW algorithm converges to a stationary point and prove that the rate of convergence is as fast as ${\cal O}( 1/\sqrt{T} )$, where
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views