
Prompt learning was proposed to solve the problem of inconsistency between the upstream and downstream tasks and has achieved State-Of-The-Art (SOTA) results in various Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks. However, Relation Extraction (RE) is more complex than other text classification tasks, which makes it more difficult to design a suitable prompt template for each dataset manually. To solve this issue, we propose a Adaptive Prompt Construction method (APC) for relation extraction.
- Categories:
 98 Views
98 Views
- Read more about PRIOR-BERT AND MULTITASK LEARNING FOR TARGET-ASPECT-SENTIMENT JOINT DETECTION
- Log in to post comments
Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis (ABSA) is a fine-grained sentiment analysis task and has become a significant task with real-world scenario value. The challenge of this task is how to generate an effective text representation and construct an end-to-end model that can simultaneously detect (target, aspect, sentiment) triples from a sentence. Besides, the existing models do not take the heavily unbalanced distribution of labels into account and also do not give enough consideration to long-distance dependence of targets and aspect-sentiment pairs.
poster-new.pdf
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views
- Read more about SCALABLE SENTIMENT FOR SEQUENCE-TO-SEQUENCE CHATBOT RESPONSE WITH PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS
- Log in to post comments
Conventional seq2seq chatbot models only try to find the sentences with the highest probabilities conditioned on the input sequences, without considering the sentiment of the output sentences. Some research works trying to modify the sentiment of the output sequences were reported. In this paper, we propose five models to scale or adjust the sentiment of the chatbot response: persona-based model, reinforcement learning, plug and play model, sentiment transformation network and cycleGAN, all based on the conventional seq2seq model.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about Towards Building a Standard Dataset for Arabic Keyphrase Extraction Evaluation
- Log in to post comments
Keyphrases are short phrases that best represent a document content. They can be useful in a variety of applications, including document summarization and retrieval models. In this paper, we introduce the first dataset of keyphrases for an Arabic document collection, obtained by means of crowdsourcing. We experimentally evaluate different crowdsourced answer aggregation strategies and validate their performances against expert annotations to evaluate the quality of our dataset. We report about our experimental results, the dataset features, some lessons learned, and ideas for future
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views
- Read more about Leveraging Arabic Morphology and Syntax for Achieving Better Keyphrase Extraction
- Log in to post comments
Arabic is one of the fastest growing languages on the Web, with an increasing amount of user generated content being published by both native and non-native speakers all over the world. Despite the great linguistic differences between Arabic and western languages such as English, most Arabic keyphrase extraction systems rely on approaches designed for western languages, thus ignoring its rich morphology and syntax. In this paper we present a new approach leveraging the Arabic morphology and syntax to generate a restricted set of meaningful candidates among which keyphrases are selected.
- Categories:
 41 Views
41 Views- Read more about Aicyber’s System for IALP 2016 Shared Task:Character-enhanced Word Vectors and Boosted Neural Networks
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views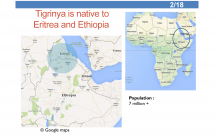
- Read more about The Effect of Shallow Segmentation for English-Tigrinya Statistical Machine Translation
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents initial English-Tigrinya statistical machine translation (SMT) research. Tigrinya is a highly inflected Semitic language spoken in Eritrea and Ethiopia. Translation involving morphologically complex languages is challenged by factors including data sparseness and source-target word alignment. We try to address these problems through morphological segmentation of Tigrinya words. After segmentation the difference in token count dropped significantly from 37.7% to 0.1%. The out-of-vocabulary rate was reduced by 46%.
IALP-tig.pdf
- Categories:
 44 Views
44 Views
We present a word sense disambiguation (WSD) tool of Japanese Hiragana words. Unlike other WSD tasks which output something like “sense #3” as result, our WSD task rewrites the target word into a Kanji word, which is a different orthography. This means that the task is also a kind of orthographical normalization as well as WSD. In this paper we present the task, our method, and the performance.
IALP-wsd.pdf
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views- Read more about Japanese Orthographical Normalization Does Not Work for Statistical Machine Translation
- Log in to post comments
We have investigated the effect of normalizing Japanese orthographical variants into a uniform orthography on statistical machine translation (SMT) between Japanese and English. In Japanese, 10% of words have reportedly more than one orthographical variants, which is a promising fact for improving translation quality when we normalize these orthographical variants.
- Categories:
 1 Views
1 Views- Read more about Fundamental Tools and Resource are Available for Vietnamese Analysis
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents our work on developing Vietnamese fundamental tools and a resource for analysis. These tools are for word segmentation and part-of-speech tagging, diacritics restoration, and orthographical variants dictionary. All of them have been either not publicly available so far or not attaining sufficient performance. We have developed the tools and released the tools to the public, in both software packages and web tools. For development, we utilize state-of-the-art methods and achieved high accuracy.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views