- Read more about A Data-Selective LS Solution to TDOA-based Source Localization
- Log in to post comments
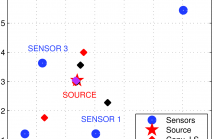
In this paper, the localization of an emitter based on Time Difference of Arrival (TDoA) has been investigated. The classical least-squares (LS) algorithm, with a limited number of TDoA measurements, has been utilized for obtaining a closed-form solution to the source localization problem. Recently, an extension of the classical LS algorithm has been employed in an attempt to improve the precision of the localization technique by using a larger set of TDoA estimates.
PosterTDOA.pdf
- Categories:
 52 Views
52 Views
This paper presents a new adaptation of a Gaussian echo model (GEM) to estimate the distances to multiple targets using acoustic signals. The proposed algorithm utilizes m-sequences and opens the door for applying other modulations and signal designs for acoustic estimation in a similar way. The proposed algorithm estimates the system impulse response and uses the GEM to limit the effect of noise before applying deconvolution to estimate the time of arrival (TOA) to multiple targets with high accuracy.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about AN EFFICIENT TARGET LOCALIZATION ESTIMATOR FROM BISTATIC RANGE AND TDOA MEASUREMENTS IN MULTISTATIC RADAR
- Log in to post comments
This paper considers the target localization problem using the hybrid bistatic range and time difference of arrival (TDOA) measurements in multistatic radar. An algebraic closed-form solution to this nonlinear estimation problem is developed through two-stage processing, where the nuisance variables are introduced in the first stage and the localization error of first stage solution is estimated to improve the final target position estimate in the second stage.
- Categories:
 58 Views
58 Views
- Read more about Distributed Linear Blind Source Separation over Wireless Sensor Networks with Arbitrary Connectivity Patterns
- Log in to post comments
Broad areal coverage and low cost make wireless sensor networks natural platforms for blind source separation (BSS). In this context, distributed processing is attractive because of low power requirements and scalability. However, existing distributed BSS algorithms either require a fully connected pattern of connectivity or require a high computational load at each sensor node. We introduce a distributed robust BSS algorithm that uses a fully shared computation and can be applied over any connected graph.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views