- Read more about A General Framework for the Design and Analysis of Sparse FIR Linear Equalizers
- Log in to post comments
Complexity of linear finite-impulse-response (FIR)
equalizers is proportional to the square of the number of nonzero
taps in the filter. This makes equalization of channels with long
impulse responses using either zero-forcing or minimum mean
square error (MMSE) filters computationally expensive. Sparse
equalization is a widely-used technique to solve this problem. In
this paper, a general framework is provided that transforms the
problem of sparse linear equalizers (LEs) design into the problem
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views- Read more about Iterative Optimization for Max-Min SINR in Dense Small-Cell Multiuser MISO SWIPT System
- Log in to post comments
GSIP_v1.pdf
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views- Read more about User Association in Small Cell Heterogeneous Network with Downlink Sum Rate
- Log in to post comments
Mixer2015.pptx
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views- Read more about Optimal Pricing for Interference Control in Time-reversal Device-to-Device Uplinks
- Log in to post comments
The Device-to-Device (D2D) communication is a promising technique to empower local wireless communications. However, without proper management it may generate interference to the existing network and degrade the overall performance. By treating each multipath as a virtual antenna, time-reversal (TR) signal transmission in a rich-scattering environment produces a spatial-temporal resonance which efficiently suppresses the inter-user interference (IUI) while boosting the signal power at the target receiver.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views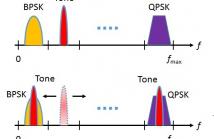
- Read more about Cyclo-Stationary based Jammer Detection Algorithm for Wide-band Radios using Compressed Sensing
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views- Read more about Exploiting Multi-Core SoC Architecture for MU-MIMO Schedulers
- Log in to post comments
Upcoming standards are moving towards multi-antenna multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) transmission techniques to harness the benefits of spatial degrees of freedom (DoF) in addition to the conventional time and frequency resources. Even though single user MIMO transmission improves the throughput noticeably, multiplexing different user data streams across the spatial dimension as in multiuser MIMO enhances the overall cell throughput significantly. However, this improved performance depends on the efficient selection of the users to be multiplexed over the spatial DoF.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views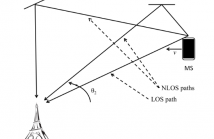
- Read more about Mixed LOS/NLOS Mobile Station Positioning Algorithm using TOA, AOA, and Doppler-Shift
- Log in to post comments
Location estimation in wireless communications systems experiencing mixed line-of-sight/non-line-of-sight (LOS/NLOS) or purely NLOS propagation paths is an open problem. In this paper, a novel least squares algorithm is presented to estimate the location of a mobile station (MS) experiencing mixed LOS/NLOS or purely NLOS communication with at least one base station (BS) by using the time of arrival (TOA), angle of arrival (AOA), and Doppler-shift (DS) measurements collected at the BS.
- Categories:
 84 Views
84 Views
- Read more about On Outage Probability for Two-Way Relay Networks with Stochastic Energy Harvesting
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose an optimal relay transmission policy by using a stochastic energy harvesting (EH) model for the EH two-way relay network, wherein the relay is solar-powered and equipped with a finite-sized battery. In this policy, the long-term outage probability is minimized by adapting the relay transmission power to the wireless channel states, battery energy amount and causal solar energy states.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about On Outage Probability for Stochastic Energy Harvesting Communications in Fading Channels
- Log in to post comments
An optimal transmission policy is considered for energy harvesting (EH) wireless point-to-point communications, wherein the source node is solar-powered and equipped with a finite-sized battery. The long-term outage probability is minimized by adapting the transmission power to the causal energy arrival information, battery energy amount and channel fading through a Markov decision process (MDP) framework.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views