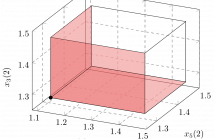
- Read more about Analysis of the Viterbi Algorithm Using Tropical Algebra and Geometry
- Log in to post comments
The Viterbi algorithm and its pruning variant, are some of the most frequently used algorithms in communications and speech recognition. There has been extended research on improving the algorithms’ computational complexity, however work trying to interpret their nonlinear structure and geometry has been limited. In this work we analyse the Viterbi algorithm in the field of tropical (min-plus) algebra, and we utilize its pruning variant in order to define a polytope. Then, we interpret certain faces of the polytope as the most probable states of the algorithm.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views
- Read more about Implementation and measurement of Power Adapted-OFDM using OpenAirInterface
- Log in to post comments
The Fifth Generation of mobile communications (5G) is being standardized in order to reach higher data rates and deploy new services. In this frame, researchers are looking for possible waveforms to improve the air interface. Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) has high Out-of-Band Emissions (OBE) which force us to leave wider guard bands, reducing so the spectral efficiency. Recently, we have proposed the Power Adapted-OFDM which is capable of fulfilling the requirements of 5G and avoids the main issues of other proposed candidates.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views
- Read more about Seismic Signal Compression Through Delay Compensated and Entropy Constrained Dictionary Learning
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose a new sparse dictionary learning scheme for lossy compression of seismic signals collected at a single sensor from multiple source shots. The method leverages the entropy constraint and delay compensation for dictionary learning. Using the proposed method for delay compensation in seismic data squeezes more redundancy out of the data which results in a sparser representation for a given dictionary. The objective of entropy constraint term in dictionary learning is to make the sparse coefficients tailored to the compression objective.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views
- Read more about Maximization of the Sum of Energy-Efficiency For Type-I HARQ Under The Rician Channel
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 1 Views
1 Views
- Read more about Random Access Schemes in Wireless Systems With Correlated User Activity
- Log in to post comments
Traditional random access schemes are designed based on the aggregate process of user activation, which is created on the basis of independent activations of the users. However, in Machine-Type Communications (MTC), some users are likely to exhibit a high degree of correlation, e.g. because they observe the same physical phenomenon. This paves the way to devise access schemes that combine scheduling and random access, which is the topic of this work. The underlying idea is to schedule highly correlated users in such a way that their transmissions are less likely to result in a collision.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about SPAWC18 - ADAPTIVE PSK MODULATION SCHEME IN THE PRESENCE OF PHASE NOISE
- Log in to post comments
Phase noise is one of the major impairments affecting severely performance of millimeter-waves (mmWaves) systems. This paper addresses the problem of link adaption for coherent and non-coherent phase modulated signals subject to phase noise. In contrast to usual link adaptation techniques, we propose a scheme exploiting an estimation of not only the Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) but also of the phase noise variance, which is essential to achieve reliable communications.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views- Read more about Digital Predistortion of Hardware Impairments for Full-Duplex Transceivers
- Log in to post comments
Digital predistortion is applied to account for all significant
hardware impairments in a regeneration architecture full-duplex
transceiver. Compared to a conventional regeneration
architecture, where non-linearities are simply reconstructed
for cancellation, by predistorting we avoid these components
to achieve an improvement in both self-interference suppression
and signal quality. A new set of predistortion basis functions
is proposed for the cascade of baseband non-linearities,
Presentation.pdf
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views- Read more about DESIGN OF BINARY LDPC CODES FOR SLEPIAN-WOLF CODING OF CORRELATED INFORMATION SOURCES
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose a scheme for distributed source coding, using low-density parity-check (LDPC) codes to compress close to the Slepian-Wolf limit for correlated binary sources. First, we develop a conventional Belief Propagation (BP) algorithm LDPC decoder which takes the syndrome information into account. Subsequently, modelling the correlation between the sources as a binary symmetric channel (BSC), we replace the received probabilities in the conventional channel with the cross over probability.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about Design of unimodular sequences with good autocorrelation and good complementary autocorrelation properties
- Log in to post comments
Complex sequences with constant magnitude in the time domain and good aperiodic autocorrelation properties are of fundamental interest due to its applications. Their design typically involves the minimization of a nonlinear function that strives to make equal to zero the correlation coefficients in a region of interest. In this letter, the design of unimodular sequences whose aperiodic autocorrelation and aperiodic complementary autocorrelation vanish for a given set of lags is proposed.
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views
- Read more about Design of unimodular sequences with good autocorrelation and good complementary autocorrelation properties
- Log in to post comments
Complex sequences with constant magnitude in the time domain and good aperiodic autocorrelation properties are of fundamental interest due to its applications. Their design typically involves the minimization of a nonlinear function that strives to make equal to zero the correlation coefficients in a region of interest. In this letter, the design of unimodular sequences whose aperiodic autocorrelation and aperiodic complementary autocorrelation vanish for a given set of lags is proposed.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views