
- Read more about ORGB: OFFSET CORRECTION IN RGB COLOR SPACE FOR ILLUMINATION-ROBUST IMAGE PROCESSING
- Log in to post comments
Single materials have colors which form straight lines in RGB space. However, in severe shadow cases, those lines do not intersect the origin, which is inconsistent with the description of most literature. This paper is concerned with the detection and correction of the offset between the intersection and origin. First, we analyze the reason for forming that offset via an optical imaging model. Second, we present a simple and effective way to detect and remove the offset.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views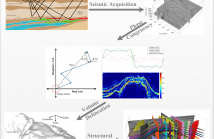
- Read more about Phase Congruency for Image Understanding with Applications in Computational Seismic Interpretation
- Log in to post comments
Phase Congruency (PC) can highlight small discontinuities in images with varying illumination and contrast using the congruency of phase in Fourier components. PC can not only detect the subtle variations in the image intensity but can also highlight the anomalous values to develop a deeper understanding of the images content and context. In this paper, we propose a new method based on PC for computational seismic interpretation with an application to subsurface structures delineation within migrated seismic volumes.
ICASSP_20170214.pdf
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views- Read more about Radioastronomical Image Reconstruction with Regularized Least Squares
- Log in to post comments
Image formation using the data from an array of sensors is a familiar problem in many fields such as radio astronomy, biomedical and geodetic imaging. The problem can be formulated as a least squares (LS) estimation problem and becomes ill-posed at high resolutions, i.e. large number of image pixels. In this paper we propose two regularization methods, one based on weighted truncation of the eigenvalue decomposition of the image deconvolution matrix and the other based on the prior knowledge of the ``dirty image" using the available data.
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views- Read more about Radioastronomical Image Reconstruction with Regularized Least Squares
- Log in to post comments
Image formation using the data from an array of sensors is a familiar problem in many fields such as radio astronomy, biomedical and geodetic imaging. The problem can be formulated as a least squares (LS) estimation problem and becomes ill-posed at high resolutions, i.e. large number of image pixels. In this paper we propose two regularization methods, one based on weighted truncation of the eigenvalue decomposition of the image deconvolution matrix and the other based on the prior knowledge of the ``dirty image" using the available data.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views- Read more about VARIATIONAL BAYESIAN IMAGE FUSION BASED ON COMBINED SPARSE REPRESENTATIONS
- Log in to post comments
Poster.pdf
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
For ICASSP 2016 paper.
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 ViewsFor ICASSP 2016 paper, "Fast Voxel Line Update for Time-Space Image Reconstruction"
- Categories:
 1 Views
1 Views
- Read more about Tomographic Reconstruction of Atmosphric Density with Mumford-Shah Functionals
- Log in to post comments
Knowledge of the three-dimensional spatial structure of Earth's uppermost atmosphere is necessary both to understand its role as a dynamic buffer against the solar-driven environment of interplanetary space as well as to assess the rate of its permanent escape from Earth's gravity through evaporation. The only available means of inferring atmospheric structure at these altitudes is through space-based remote sensing of solar radiation that is resonantly scattered or fluoresced by the ambient atoms.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about Spatial Stimuli Gradient Sketch Model
- Log in to post comments
The inability of automated edge detection methods inspired from primal sketch models to accurately calculate object edges under the influence of pixel noise is an open problem. Extending the principles of image perception i.e. Weber-Fechner law, and Sheperd similarity law, we propose a new edge detection method and formulation that use perceived brightness and neighbourhood similarity calculations in the determination of robust object edges.
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 Views
- Read more about Augmented Lagrangian without alternating directions: practical algorithms for inverse problems in imaging
- Log in to post comments
Several problems in signal processing and machine learning can be casted as optimization problems. In many cases, they are of large-scale, nonlinear, have constraints, and nonsmooth in the unknown parameters. There exists plethora of fast algorithms for smooth convex optimization, but these algorithms are not readily applicable to nonsmooth problems, which has led to a considerable amount of research in this direction. In this paper, we propose a general algorithm for nonsmooth bound-constrained convex optimization problems.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 ViewsPages
- « first
- ‹ previous
- 1
- 2
- 3