
- Read more about Deep Ptych: Subsampled Fourier Ptychography Using Deep Generative Priors
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes a novel framework to regularize the highly illposed and non-linear Fourier ptychography problem using generative models. We demonstrate experimentally that our proposed algorithm, Deep Ptych, outperforms the existing Fourier ptychography techniques, in terms of quality of reconstruction and robustness against noise, using far fewer samples. We further modify the proposed approach to allow the generative model to explore solutions outside the range, leading to improved performance.
- Categories:
 63 Views
63 Views
Material aging has a significant effect on the realistic rendering of artwork objects. Small deformations of the surface structure, color or texture variations contribute to the realistic look of artwork objects. These aging effects depend on material composition, object usage, weathering conditions, and a large number of other physical, biological, and chemical parameters.
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views
- Read more about Sub-diffraction Imaging using Fourier Ptychography and Structured Sparsity
- Log in to post comments
We consider the problem of super-resolution for sub-diffraction imaging. We adapt conventional Fourier ptychographic approaches, for the case where the images to be acquired have an underlying structured sparsity. We propose some sub-sampling strategies which can be easily adapted to existing ptychographic setups. We then use a novel technique called CoPRAM with some modifications, to recover sparse (and block sparse) images from sub-sampled ptychographic measurements.
- Categories:
 31 Views
31 Views
- Read more about High-speed light field image formation analysis using wavefield modeling with flexible sampling
- Log in to post comments
In order to understand the image formation inside plenoptic systems, a wave-optic-based model is proposed in this paper that uses the Fresnel diffraction equation to propagate the whole object field into the plenoptic systems. The proposed model is much flexible at sampling on propagation planes by utilizing the method of multiple partial propagations. In order to verify the effectiveness of the proposed model, numerical simulations are conducted by comparing with existing wave optic model under different optical configurations of plenoptic cameras.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views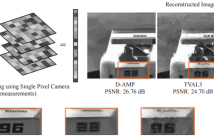
Reconstruction of signals from compressively sensed measurements is an ill-posed problem. In this paper, we leverage the recurrent generative model, RIDE, as an image prior for compressive image reconstruction. Recurrent networks can model long-range dependencies in images and hence are suitable to handle global multiplexing in reconstruction from compressive imaging. We perform MAP inference with RIDE using back-propagation to the inputs and projected gradient method. We propose an entropy thresholding based approach for preserving texture in images well.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views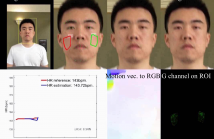
- Read more about Fitness Heart Rate Measurement Using Face Videos
- Log in to post comments
Recent studies showed that subtle changes in human’s face color due to the heartbeat can be captured by digital video recorders. Most work focused on still/rest cases or those with relatively small motions. In this work, we propose a heart-rate monitoring method for fitness exercise videos. We focus on building a highly precise motion compensation scheme with the help of the optical flow, and use motion information as a cue to adaptively remove ambiguous frequency components for improving the heart rates estimates.
- Categories:
 552 Views
552 Views
- Read more about LOW COMPLEXITY IMAGE FUSION IN BAYER DOMAIN USING A MONOCHROME SENSOR AND BAYER SENSOR
- Log in to post comments
Mobile cameras have come a long way since their evolution and have replaced digital still cameras. However, their lowlight photography performance needs significant improvement. Dual camera systems consisting of a monochrome sensor and a Bayer sensor offer us a way to improve the low-light photography. The existing dual camera systems use post-processing methods after Image Signal Processor (ISP) for image fusion which are computationally intensive and use two ISPs. We propose a novel architecture in which the image fusion can be done in Bayer domain prior to the ISP.
- Categories:
 52 Views
52 Views