
- Read more about INVESTIGATING ROBUSTNESS OF UNSUPERVISED STYLEGAN IMAGE RESTORATION
- Log in to post comments
Recently, generative priors have shown significant improvement for unsupervised image restoration. This study explores the incorporation of multiple loss functions that capture various perceptual and structural aspects of image quality. Our proposed method improves robustness across multiple tasks, including denoising, upsampling, inpainting, and deartifacting, by utilizing a comprehensive loss function based on Learned Perceptual Image Patch Similarity(LPIPS), Multi-Scale Structural Similarity Index Measure Loss(MS-SSIM), Consistency, Feature, and Gradient losses.
- Categories:
 54 Views
54 Views
- Read more about Supplementary Material
- Log in to post comments
HOW SHOULD WE EVALUATE DATA DELETION IN GRAPH-BASED ANN INDEXES ?
- Categories:
 52 Views
52 Views
- Read more about Supplementary - Towards Image Copy Detection at E-commerce Scale
- Log in to post comments
Copy Detection system aims to identify if a query image is an edited/manipulated copy of an image from a large reference database with millions of images. While global image descriptors can retrieve visually similar images, they struggle to differentiate near-duplicates from semantically similar instances. We propose a dual-triplet metric learning (DTML) technique to learn global image features that group near-duplicates closer than visually similar images while maintaining the semantic structure of the embedding space.
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views
ICIP2025_1674_supplementary-material_Multi_Res_3DGS
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views
- Read more about TEMPORAL TRANSFORMER ENCODER FOR VIDEO CLASS INCREMENTAL LEARNING
- Log in to post comments
Current video classification approaches suffer from catastrophic forgetting when they are retrained on new databases.
Continual learning aims to enable a classification system with learning from a succession of tasks without forgetting.
In this paper we propose to use a transformer-based video class incremental learning model. During a succession of
learning steps, at each training time, the transformer is used to extract characteristic spatio-temporal features from videos
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views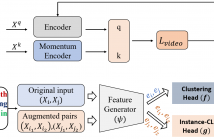
- Read more about ICASSP2024-Paper ID 3371-IVMSP-L2.4: VT-REID: LEARNING DISCRIMINATIVE VISUAL-TEXT REPRESENTATION FOR POLYP RE-IDENTIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
Presention Slides in ICASSP2024 for IVMSP-L2.4: VT-REID: LEARNING DISCRIMINATIVE VISUAL-TEXT REPRESENTATION FOR POLYP RE-IDENTIFICATION
- Categories:
 37 Views
37 Views
- Read more about PART REPRESENTATION LEARNING WITH TEACHER-STUDENT DECODER FOR OCCLUDED PERSON RE-IDENTIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
Occluded person re-identification (ReID) is a very challenging task due to the occlusion disturbance and incomplete target information. Leveraging external cues such as human pose or parsing to locate and align part features has been proven to be very effective in occluded person ReID. Meanwhile, recent Transformer structures have a strong ability of long-range modeling. Considering the above facts, we propose a Teacher-Student Decoder (TSD) framework for occluded person ReID, which utilizes the Transformer decoder with the help of human parsing.
- Categories:
 98 Views
98 Views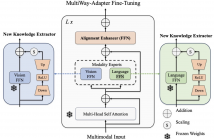
- Read more about MultiWay-Adapter: Adapting Multimodal Large Language Models for scalable image-text retrieval
- Log in to post comments
As Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) grow in size, adapting them to specialized tasks becomes increasingly challenging due to high computational and memory demands. While efficient adaptation methods exist, in practice they suffer from shallow inter-modal alignment, which severely hurts model effectiveness. To tackle these challenges, we introduce the MultiWay-Adapter (MWA), which deepens inter-modal alignment, enabling high transferability with minimal tuning effort.
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views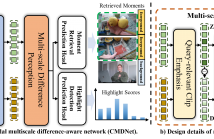
- Read more about Cross-modal Multiscale Difference-aware Network for Joint Moment Retrieval and Highlight Detection
- Log in to post comments
Since the goals of both Moment Retrieval (MR) and Highlight Detection (HD) are to quickly obtain the required content from the video according to user needs, several works have attempted to take advantage of the commonality between both tasks to design transformer-based networks for joint MR and HD. Although these methods achieve impressive performance, they still face some problems: \textbf{a)} Semantic gaps across different modalities. \textbf{b)} Various durations of different query-relevant moments and highlights. \textbf{c)} Smooth transitions among diverse events.
CMDNet_04_13.pdf
- Categories:
 46 Views
46 Views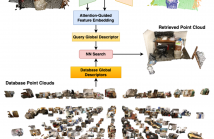
- Read more about AEGIS-Net: Attention-Guided Multi-Level Feature Aggregation for Indoor Place Recognition
- Log in to post comments
We present AEGIS-Net, a novel indoor place recognition model that takes in RGB point clouds and generates global place descriptors by aggregating lower-level color, geometry features and higher-level implicit semantic features. However, rather than simple feature concatenation, self-attention modules are employed to select the most important local features that best describe an indoor place. Our AEGIS-Net is made of a semantic encoder, a semantic decoder and an attention-guided feature embedding.
Poster.pdf
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views