- Read more about ADAPTIVE CODING OF NON-NEGATIVE FACTORIZATION PARAMETERS WITH APPLICATION TO INFORMED SOURCE SEPARATION
- Log in to post comments
Informed source separation (ISS) uses source separation for extracting audio objects out of their downmix given some pre-computed parameters. In recent years, non-negative tensor factorization (NTF) has proven to be a good choice for compressing audio objects at an encoding stage. At the decoding stage, these parameters are used to separate the downmix with Wiener-filtering. The quantized NTF parameters have to be encoded to a bitstream prior to transmission.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views- Read more about Decorrelation for Audio Object Coding
- Log in to post comments
Object-based representations of audio content are increasingly
used in entertainment systems to deliver immersive and
personalized experiences. Efficient storage and transmission
of such content can be achieved by joint object coding algorithms
that convey a reduced number of downmix signals
together with parametric side information that enables object
reconstruction in the decoder. This paper presents an
approach to improve the performance of joint object coding
by adding one or more decorrelators to the decoding process.
- Categories:
 41 Views
41 Views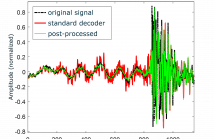
- Read more about Pre-Echo Noise Reduction in Frequency-Domain Audio Codecs (Poster)
- Log in to post comments
One of the most common yet detrimental compression artifacts in frequency-domain audio codecs is known as pre-echo, which is perceived as a brief noise preceding transient signals, and is discernable even without direct comparison to the original signal. Because of its substantial negative impact on audio quality, many techniques have been proposed to alleviate it, but not without effect on coding efficiency.
jim-poster.pdf
- Categories:
 52 Views
52 Views- Read more about Adaptive selection of lag-window shape for linear predictive analysis in the 3GPP EVS codec
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views- Read more about A PACKET LOSS RECOVERY TECHNIQUE WITH LINE SPECTRAL FREQUENCY MODIFICATION IN 3GPP EVS CODEC
- Log in to post comments
This paper examines a method for controlling the energy of decoded signal at the recovery frame from a packet loss. Our observation unveiled that a packet loss around speech onset causes sudden increase in the amplitude of the decoded signal at the recovery frame. To mitigate the artifact caused by the overshoot, a detector of the speech overshoot is proposed as well as a method that controls the amplitude of the decoded signal by adjusting distances of adjacent line spectral frequencies.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views- Read more about DELAY-LESS FREQUENCY DOMAIN PACKET-LOSS CONCEALMENT FOR TONAL AUDIO SIGNALS
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views
This presentation describes the bandwidth extension (BWE) method developed for the AMR-WB interoperable (AMR-WB IO) modes of the 3GPP EVS codec. The low-band signal (0-6.4 kHz) is coded using an enhanced version of ACELP as in AMR-WB and post-processed; the high-band (above 6.4 kHz) in contrast to AMR-WB is represented with a new BWE method. The decoded low-band excitation is adaptively extended to high frequencies and filtered in the DCT domain. The extended excitation is scaled by subframe gains and shaped by a weighted LPC synthesis filter.
- Categories:
 200 Views
200 Views
- Read more about A Novel Frequency Domain BWE with Relaxed Synchronization and Associated BWE Switching
- Log in to post comments
This presentation describes a novel frequency domain bandwidth extension (BWE) scheme with relaxed synchronization, optimized for coding inactive and music/mixed content signals. The algorithm achieves high subjective quality at low and medium bitrates and it has a low algorithmic delay. The algorithm is part of the 3GPP Enhanced Voice Services (EVS) codec. In addition to the presented algorithm, the EVS codec employs also a time domain BWE scheme optimized for active speech coding.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Read more about Audio Bandwidth Detection in the EVS Codec
- Log in to post comments
Speech and audio codecs are usually designed such that they encode all the frequency bands of the input signal spectrum. If the higher bands do not contain any perceptually meaningful content, these codecs often do not work optimally as they assign part of the available bit budget to encode these bands. In this paper we describe a bandwidth detection algorithm that determines the effective audio bandwidth of the input signal.
- Categories:
 73 Views
73 Views
- Read more about Linear estimation based primary-ambient extraction for stereo audio signals (slides)
- Log in to post comments
Audio signals for moving pictures and video games are often linear combinations of primary and ambient components. In spatial audio analysis-synthesis, these mixed signals are usually decomposed into primary and ambient components to facilitate flexible spatial rendering and enhancement. Existing approaches such as principal component analysis (PCA) and least squares (LS) are widely used to perform this decomposition from stereo signals.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views