
- Read more about FOREGROUND HARMONIC NOISE REDUCTION FOR ROBUST AUDIO FINGERPRINTING
- Log in to post comments
Audio fingerprinting systems are often well designed to cope with a range of broadband noise types however they cope less well when presented with additive noise containing sinusoidal components. This is largely due to the fact that in a short-time signal representa- tion (over periods of ≈ 20ms) these noise components are largely indistinguishable from salient components of the desirable signal that is to be fingerprinted.
Draft_v2.pdf
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about FOREGROUND HARMONIC NOISE REDUCTION FOR ROBUST AUDIO FINGERPRINTING
- Log in to post comments
Audio fingerprinting systems are often well designed to cope with a range of broadband noise types however they cope less well when presented with additive noise containing sinusoidal components. This is largely due to the fact that in a short-time signal representa- tion (over periods of ≈ 20ms) these noise components are largely indistinguishable from salient components of the desirable signal that is to be fingerprinted.
Draft_v2.pdf
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views
- Read more about Depression Speaks: Automatic Discrimination Between Depressed and Non-Depressed Speakers Based on Nonverbal Speech Features
- Log in to post comments
This article proposes an automatic approach - based on nonverbal speech features - aimed at the automatic discrimination between depressed and non-depressed speakers. The experiments have been performed over one of the largest corpora collected for such a task in the literature ($62$ patients diagnosed with depression and $54$ healthy control subjects), especially when it comes to data where the depressed speakers have been diagnosed as such by professional psychiatrists.
icassp.pdf
- Categories:
 67 Views
67 Views- Read more about A First Attempt at Polyphonic Sound Event Detection Using Connectionist Temporal Classification
- Log in to post comments
Sound event detection is the task of detecting the type, starting time, and ending time of sound events in audio streams. Recently, recurrent neural networks (RNNs) have become the mainstream solution for sound event detection. Because RNNs make a prediction at every frame, it is necessary to provide exact starting and ending times of the sound events in the training data, making data annotation an extremely time-consuming process.
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views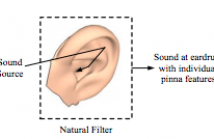
- Read more about Natural Sound Rendering for Headphones: Integration of signal processing techniques
- Log in to post comments
With the strong growth of assistive and personal listening devices, natural sound rendering over headphones is becoming a necessity for prolonged listening in multimedia and virtual reality applications. The aim of natural sound rendering is to naturally recreate the sound scenes with the spatial and timbral quality as natural as possible, so as to achieve a truly immersive listening experience. However, rendering natural sound over headphones encounters many challenges. This tutorial article presents signal processing techniques to tackle these challenges to assist human listening.
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views