
- Read more about Common-slope modeling of late reverberation
- Log in to post comments
The decaying sound field in rooms is typically described by energy decay functions (EDFs). Late reverberation can deviate considerably from the ideal diffuse field, for example, in multiple connected rooms or non-uniform absorption material distributions. This paper proposes the common-slope model of late reverberation. The model describes spatial and directional late reverberation as linear combinations of exponential decays called common slopes.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Read more about Spatial Scaper: A Library to Simulate and Augment Soundscapes for Sound Event Localization and Detection in Realistic Rooms
- Log in to post comments
Sound event localization and detection (SELD) is an important task in machine listening.
Major advancements rely on simulated data with sound events in specific rooms and strong spatio-temporal labels.
SELD data is simulated by convolving spatialy-localized room impulse responses (RIRs) with sound waveforms to place sound events in a soundscape.
However, RIRs require manual collection in specific rooms.
We present SpatialScaper, a library for SELD data simulation and augmentation.
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views
- Read more about DUAL-PATH MINIMUM-PHASE AND ALL-PASS DECOMPOSITION NETWORK FOR SINGLE CHANNEL SPEECH DEREVERBERATION
- Log in to post comments
Introduction of DUAL-PATH MINIMUM-PHASE AND ALL-PASS DECOMPOSITION NETWORK FOR SINGLE CHANNEL SPEECH DEREVERBERATION.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views
- Read more about Unsupervised Acoustic Scene Mapping Based on Acoustic Features and Dimensionality Reduction
- Log in to post comments
Classical methods for acoustic scene mapping require the estimation of the time difference of arrival (TDOA) between microphones. Unfortunately, TDOA estimation is very sensitive to reverberation and additive noise. We introduce an unsupervised data-driven approach that exploits the natural structure of the data. Toward this goal, we adapt the recently proposed local conformal autoencoder (LOCA) – an offline deep learning scheme for extracting standardized data coordinates from measurements.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views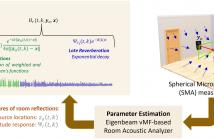
- Read more about Room Impulse Response Reconstruction Based on Spatio-Temporal-Spectral Features Learned from a Spherical Microphone Array Measurement
- Log in to post comments
Large-scale Room Impulse Response (RIR) measurements are required to accurately determine a room's acoustic response to different source-listener configurations. RIR reconstruction methods are often used to reduce these measurement costs. Prior knowledge of room acoustic parameters can ensure reliable and robust RIR reconstruction. This paper proposes a method to reconstruct RIRs based on reflection source locations and time-frequency-direction-dependent reflection magnitude response estimated from a single spherical microphone array measurement.
- Categories:
 74 Views
74 Views
- Read more about The R3VIVAL Dataset: Repository of room responses and 360 videos of a variable acoustics lab
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents a dataset of spatial room impulse responses (SRIRs) and 360° stereoscopic video captures of a variable acoustics laboratory. A total of 34 source positions are measured with 8 different acoustic panel configurations, resulting in a total of 272 SRIRs. The source positions are arranged in 30° increments at concentric circles of radius 1.5, 2, and 3 m measured with a directional studio monitor, as well as 4 extra positions at the room corners measured with an omnidirectional source.
Poster.pdf
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views
Despite there being clear evidence for attentional effects in biological spatial hearing, relatively few machine hearing systems exploit attention in binaural sound localisation. This paper addresses this issue by proposing a novel binaural machine hearing system with temporal attention for robust localisation of sound sources in noisy and reverberant conditions. A convolutional neural network is employed to extract noise-robust localisation features, which are similar to interaural phase difference, directly from phase spectra of the left and right ears for each frame.
- Categories:
 58 Views
58 Views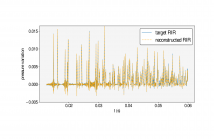
- Read more about Gridless 3D Recovery of Image Sources from Room Impulse Responses
- Log in to post comments
Given a sound field generated by a sparse distribution of impulse image sources, can the continuous 3D positions and amplitudes of these sources be recovered from discrete, band-limited measurements of the field at a finite set of locations, e.g. , a multichannel room impulse response? Borrowing from recent advances in super-resolution imaging, it is shown that this non-linear, non-convex inverse problem can be efficiently relaxed into a convex linear inverse problem over the space of Radon measures in R^3 .
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views
Low frequency personal sound zones can be created by controlling the sound pressure in separate spatially confined regions. The performance of a sound zone system using wireless communication may be degraded due to potential packet losses. In this paper, we propose robust FIR filters for low-frequency sound zone system by incorporating information about the expected packet losses into the design.
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views
- Read more about Kernel interpolation of acoustic transfer functions with adaptive kernel for directed and residual reverberations
- Log in to post comments
An interpolation method for region-to-region acoustic transfer functions (ATFs) based on kernel ridge regression with an adaptive kernel is proposed. Most current ATF interpolation methods do not incorporate the acoustic properties for which measurements are performed. Our proposed method is based on a separate adaptation of directional weighting functions to directed and residual reverberations, which are used for adapting kernel functions. Thus, the proposed method can not only impose constraints on fundamental acoustic properties, but can also adapt to the acoustic environment.
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views