
- Read more about Human emotion recognition using multi-modal biological signals based on time lag-considered correlation maximization
- Log in to post comments
A human emotion recognition using multi-modal biological signals based on time lag-considered correlation maximization is presented in this paper. Various multi-modal emotion recognition methods for visual stimuli have been studied and they focus on gaze and brain activity data. The visual stimuli captured by human eyes are sent to the brain by neurotransmitters. Thus, there is a time lag between gaze data, which record where humans gaze at, and brain activity data. However, most of the previous methods only integrate features obtained from each data without considering such a time lag.
- Categories:
 141 Views
141 Views

- Read more about DENOISING OF EVENT-BASED SENSORS WITH SPATIAL-TEMPORAL CORRELATION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 66 Views
66 Views
- Read more about A MULTI-PERSPECTIVE APPROACH TO ANOMALY DETECTION FOR SELF-AWARE EMBODIED AGENTS
- Log in to post comments
This paper focuses on multi-sensor anomaly detection for moving cognitive agents using both external and private first-person visual observations. Both observation types are used to characterize agents’ motion in a given environment. The proposed method generates locally uniform motion models by dividing a Gaussian process that approximates agents’ displacements on the scene and provides a Shared Level (SL) self-awareness based on Environment Centered (EC) models.
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views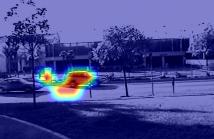
- Read more about Unsupervised Estimation Of Uncertainty For Video Saliency Detection Using Temporal Cues
- Log in to post comments
Presentation Slides for "Unsupervised Estimation Of Uncertainty For Video Saliency Detection Using Temporal Cues" at GlobalSIP 2015
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views