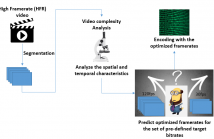
- Read more about CODA: Content-aware Frame Dropping Algorithm for High Frame-rate Video Streaming
- Log in to post comments
High Framerate (HFR) video streaming enhances the viewing experience and improves visual clarity. However, it may lead to an increase of both encoding time complexity and compression artifacts at lower bitrates. To address this challenge, this paper proposes a content-aware frame dropping algorithm (CODA) to drop frames uniformly in every video (segment) according to the target bitrate and the video characteristics.
- Categories:
 126 Views
126 Views
- Read more about RNNSC: Recurrent Neural Network Based Stereo Compression Using Image and State Warping
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 35 Views
35 Views
- Read more about Synergies between in-loop and out-of-loop mapping for HDR-PQ content
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents experimental results related to adaptive video content mapping used as a compression tool for HDR-PQ content. The purpose of adaptive video content mapping is to adapt the video signal dynamically depending on its statistical properties in order to better exploit the signal codewords range. Adaptive video content mapping has been investigated during the Versatile Video Coding (VVC) standard development with two main implementation designs: in-loop mapping, and out-of-loop mapping.
- Categories:
 35 Views
35 Views
- Read more about Beyond Keypoint Coding: Temporal Evolution Inference with Compact Feature Representation for Talking Face Video Compression
- Log in to post comments
We propose a talking face video compression framework by implicitly transforming the temporal evolution into compact feature representation. More specifically, the temporal evolution of faces, which is complex, non-linear and difficult to extrapolate, is modelled in an end-to-end inference framework based upon very compact features. This enables the high-quality rendering of the face videos, which benefits from the learning of dense motion map with compact feature representation.
- Categories:
 99 Views
99 Views
- Read more about Compressing Cipher Images by Using Semi-tensor Product Compressed Sensing and Pre-mapping
- Log in to post comments
As a new signal processing technology, compressed sensing (CS) has been showed to be a promising solution for compressing cipher images. However, the previous CS-based schemes are unsatisfactory in terms of ratio-distortion (R-D) performance. In order to solve this problem, an image encryption-then-compression (ETC) scheme by using semi-tensor product CS (STP-CS) and pre-mapping is proposed in this paper. In the proposed scheme, the original image is encrypted by using the scrambling operation. After image encryption, the cipher image is compressed through three steps.
DCC 2022.pdf
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 Views
- Read more about Semantic Neural Rendering-based Video Coding: Towards Ultra-Low Bitrate Video Conferencing
- Log in to post comments
DCC-Pre.pptx
- Categories:
 57 Views
57 Views
- Read more about Pathology Image Compression Based on JPEG2000, Multi-Resolutional Human Perception and the Region of Interest Predictions
- Log in to post comments
To achieve high efficiency of remote pathology image browsing in telemedicine, efficient image compression coding is required. In this work, we establish a visibility threshold (VT) model, which considers multi-resolution and different visual qualities jointly. Based on this model, we propose an image coding method under the JPEG2000 standard for the whole-slide pathology images (WSIs), which operates adaptively according to the required resolutions and visual qualities.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views
- Read more about Coarse-to-fine Prediction With Local and Nonlocal Correlations for Intra Coding
- Log in to post comments
Recently many efforts have been devoted to learning non-linear predictions from neighboring samples with deep neural networks. However, existing methods mainly generate predictions with local reference samples, regardless of nonlocal self-similarity.
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views
- Read more about Attribute-Decomposable Motion Compression Network for 3D MoCap Data
- Log in to post comments
Motion Capture (MoCap) data is one type of fundamental asset for the digital entertainment. The progressively increasing 3D applications make MoCap data compression unprecedentedly important. In this paper, we propose an end-to-end attribute-decomposable motion compression network using the AutoEncoder architecture. Specifically, the algorithm consists of an LSTM-based encoder-decoder for compression and decompression. The encoder module decomposes human motion into multiple uncorrelated semantic attributes, including action content, arm space, and motion mirror.
- Categories:
 159 Views
159 Views
- Read more about Improved Deep Image Compression with Joint Optimization of Cross Channel Context Model And Generalized Loop Filter
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 97 Views
97 Views