
- Read more about Occupancy Map Guided Attributes Deblocking for Video-based Point Cloud Compression CONTENT VIDEO
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 51 Views
51 Views
- Read more about Novel Foreground and Background Separation Based Multi-level Coding Framework for Indoor Surveillance Video
- Log in to post comments
There is larger compression potential for surveillance video coding due to the inherent superredundancy in fixed camera scenarios, which is not fully utilized in the general-purpose MPEG-like video coders. In this paper, we propose a novel compression framework for indoor surveillance video in which the background and foreground humans are separately compressed. Since the indoor surveillance video’s background is static, the background is extracted and shared between frames.
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 Views
In the paper highly ecient algorithm for lossless image coding is described. Its high data compaction performance is obtained at the expense of computational complexity, still being not as high as for other top rated methods. The algorithm is based on predictor blending principle, outputs of 27 dierent sub-predictors are combined, hence its name Blend-27. Eciency of Blend-27 is tested on a set of 15 usually used benchmark images, and compared to that of over 20 methods, including the best known ones.
- Categories:
 41 Views
41 Views
- Read more about A Spatial-Focal Error Concealment Scheme for Corrupted Focal Stack Video
- Log in to post comments
Focal stack image sequences can be regarded as successive frames of videos, which are densely captured by focusing on a stack of focal planes. This type of data is able to provide focus cues for display technologies. Before the displays on the user side, focal stack video is possibly corrupted during compression, storage and transmission chains, generating error frames on the decoder side. The error regions are difficult to be recovered due to the focal changes among frames.
- Categories:
 71 Views
71 Views
- Read more about Point Cloud Geometry Compression via Density-Constrained Adaptive Graph Convolution
- Log in to post comments
With the rapid development of 3D vision applications such as autonomous driving and the dramatic increase of point cloud data, it becomes critical to efficiently compress 3D point clouds. Recently, point-based point cloud compression has attracted great attention due to its superior performance at low bit rates. However, lacking an efficient way to represent the local geometric correlation well, most existing methods can hardly extract fine local features accurately. Thus it’s difficult for them to obtain high-quality reconstruction of local geometry of point clouds.
- Categories:
 44 Views
44 Views
- Read more about Semantically Adaptive JND Modeling with Object-wise Feature Characterization and Cross-object Interaction
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
- Read more about Multi_Scale Information Can Do More: Attention Aggregation Mechanism for Image Compression
- Log in to post comments
The semantic information obtained from large-scale computation in image compression is not practical. To solve this problem, we propose an Attention Aggregation Mechanism (AAM) for learning-based image compression, which is able to aggregate attention map from multiple scales and facilitate information embedding.
- Categories:
 71 Views
71 Views
- Read more about CNN Quadtree Depth Decision Prediction for Block Partitioning in HEVC Intra-Mode
- Log in to post comments
High Efficiency Video Coding. (HEVC) is the product of a large collaborative effort from industry and academic community and reflects the new international standardization for digital video coding technology. Compression capability is the main goal behind the digital video compression technology. HEVC achieves this goal at the expense of dramatically increasing coding complexity. One such area of increased complexity is due to the use of a recursive quad-tree to partition every frame to various block sizes, a process called prediction mode.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views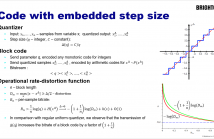
- Read more about Block Codes with Embedded Quantization Step Size Information
- Log in to post comments
If we quantize a block of n samples and then transmit information about quantization step size in the same bitstream, we may naturally expect such a code to be at least O(1/n) redundant. However, as we will show in this paper, this may not necessarily be true. Moreover, we prove that asymptotically, such codes can be as efficient as block codes without embedded step-size information. The proof relies on results from the Diophantine approximations theory. We discuss the significance of this finding for practical applications, such as the design of audio and video coding algorithms.
- Categories:
 103 Views
103 Views
- Read more about NOVEL INSTANCE MINING WITH PSEUDO-MARGIN EVALUATION FOR FEW-SHOT OBJECT DETECTION
- Log in to post comments
Few-shot object detection (FSOD) enables the detector to recognize novel objects only using limited training samples, which could greatly alleviate model’s dependency on data. Most existing methods include two training stages, namely base training and fine-tuning. However, the unlabeled novel instances in the base set were untouched in previous works, which can be re-used to enhance the FSOD performance. Thus, a new instance mining model is proposed in this paper to excavate the novel samples from the base set. The detector is thus fine-tuned again by these additional free novel instances.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 49 Views
49 Views