- Read more about IMAGE-BASED PM2.5 ESTIMATION AND ITS APPLICATION ON DEPTH ESTIMATION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views
- Read more about Joint License Plate Super-Resolution and Recognition in One Multi-Task GAN Framework
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 50 Views
50 Views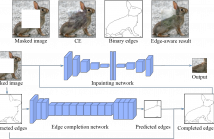
- Read more about Edge-aware Context Encoder for Image Inpainting
- Log in to post comments
We present Edge-aware Context Encoder (E-CE): an image inpainting model which takes scene structure and context into account. Unlike previous CE which predicts the missing regions using context from entire image, E-CE learns to recover the texture according to edge structures, attempting to avoid context blending across boundaries. In our approach, edges are extracted from the masked image, and completed by a full-convolutional network. The completed edge map together with the original masked image are then input into the modified CE network to predict the missing region.
- Categories:
 261 Views
261 Views
- Read more about Spatiotemporal Attention Based Deep Neural Networks for Emotion Recognition
- Log in to post comments
We propose a spatiotemporal attention based deep neural networks for dimensional emotion recognition in facial videos. To learn the spatiotemporal attention that selectively focuses on emotional sailient parts within facial videos, we formulate the spatiotemporal encoder-decoder network using Convolutional LSTM (ConvLSTM)modules, which can be learned implicitly without any pixel-level annotations. By leveraging the spatiotemporal attention, we also formulate the 3D convolutional neural networks (3D-CNNs) to robustly recognize the dimensional emotion in facial videos.
- Categories:
 84 Views
84 Views
- Read more about SPARSE DISPARITY ESTIMATION USING GLOBAL PHASE ONLY CORRELATION FOR STEREO MATCHING ACCELERATION
- Log in to post comments
In this study, we propose an efficient stereo matching method which estimates sparse disparities using global phase only correlation (POC). Conventionally, cost functions are to be calculated for all disparity candidates and the associated computational cost has been impediment in achieving a real-time performance. Therefore, we consider to use fullimage 2D phase only correlation (FIPOC) for detecting the valid disparity candidates. This will require comparatively fewer calculations for the same number of disparity.
- Categories:
 46 Views
46 Views
Performance-cost trade-offs in video object tracking tasks for long video sequences is investigated. A novel frame-subsampled, drift-resilient (FSDR) video object tracking algorithm is presented that would achieve desired tracking accuracy while dramatically reducing computing time by processing only sub-sampled video frames. A new pattern matching score metric is proposed to estimate the probability of drifting. A drift-recovery procedure is developed to enable the algorithm to recover from a drift situation and resume accurate tracking.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about Learning convolutional sparse coding
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
We propose a convolutional recurrent sparse auto-encoder
model. The model consists of a sparse encoder, which is a
convolutional extension of the learned ISTA (LISTA) method,
and a linear convolutional decoder. Our strategy offers a simple
method for learning a task-driven sparse convolutional
dictionary (CD), and producing an approximate convolutional
sparse code (CSC) over the learned dictionary. We trained
the model to minimize reconstruction loss via gradient decent
with back-propagation and have achieved competitve
- Categories:
 38 Views
38 Views
- Read more about Document Quality Estimation using Spatial Frequency Response
- Log in to post comments
The current Document Image Quality Assessment (DIQA) algorithms directly relate the Optical Character Recognition (OCR) accuracies with the quality of the document to build supervised learning frameworks. This direct correlation has two major limitations: (a) OCR may be affected by factors independent of the quality of the capture and (b) it cannot account for blur variations within an image. An alternate possibility is to quantify the quality of capture using human judgement, however, it is subjective and prone to error.
rai_ICASSP.pdf
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views
- Read more about PREDICTING TONGUE MOTION IN UNLABELED ULTRASOUND VIDEO USING 3D CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
A 3-dimensional convolutional neural network is trained on unlabeled ultrasound video to predict an upcoming tongue image from previous ones. The network obtains results superior to those of simpler predictors, and provides a starting point for exploiting the higher-level representation of the tongue learned by the system in a variety of applications in speech research. This work is believed to be the first application of convolutional neural networks to unlabeled ultrasound video for the purpose of predicting tongue movement.
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views
- Read more about Hard Shadows Removal Using An Approximate Illumination Invariant
- Log in to post comments
Hard shadows detection and removal from foreground masks is a challenging step in change detection. This paper gives a simple and effective method to address hard shadows. There are inside portion and boundary portion in hard shadows. Pixel-wise neighborhood ratio is calculated to remove the most of inside shadow points. For the boundaries of shadow regions, we take advantage of color constancy to eliminate the edges of hard shadows and obtain relative accurate objects contours. Then, morphology processing is explored to enhance the integrity of objects.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views