
In this paper we propose a method to segment individual leaves of crop plants from UAV imagery for the purposes of deriving phenotypic properties of the plant. The crop plant used in our study is sorghum Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench. Phenotyping is a set of methodologies for analyzing and obtaining characteristic traits of a plant. In a phenotypic study, leaves are often used to estimate traits such as individual leaf area and Leaf Area Index (LAI). Our approach is to segment the leaves in polar coordinates using the plant center as the origin.
- Categories:
 78 Views
78 Views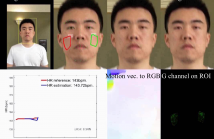
- Read more about Fitness Heart Rate Measurement Using Face Videos
- Log in to post comments
Recent studies showed that subtle changes in human’s face color due to the heartbeat can be captured by digital video recorders. Most work focused on still/rest cases or those with relatively small motions. In this work, we propose a heart-rate monitoring method for fitness exercise videos. We focus on building a highly precise motion compensation scheme with the help of the optical flow, and use motion information as a cue to adaptively remove ambiguous frequency components for improving the heart rates estimates.
- Categories:
 547 Views
547 Views
- Read more about Mondrian Stereo
- Log in to post comments
Untextured scenes with complex occlusions still present challenges to modern stereo algorithms. We consider the pathological case of Mondrian Stereo—scenes consisting solely of solid-colored planar regions, inspired by paintings by Piet Mondrian. We analyze assumptions that allow disambiguating such scenes and present a novel stereo algorithm employing symbolic reasoning about matched edge segments. We demonstrate compelling stereo matching results on synthetic scenes and discuss how our insights could be utilized in robust real-world stereo algorithms for untextured environments.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about FULLY AUTOMATED HIGHLY ACCURATE 3D RECONSTRUCTION FROM MULTIPLE VIEWS
- Log in to post comments
The reconstruction of real world objects becomes even more important in the view of creating highly realistic scenes for Virtual Reality applications. In this paper, we present a fully automated algorithmic pipeline for high-quality 3D reconstruction of real world objects. The proposed method refines an initial 3D model by exploiting the results of additional pairwise stereo depth estimation. An automatic camera selection approach provides different point clouds, which are fused into a common coherent and highly detailed 3D model.
- Categories:
 41 Views
41 Views- Read more about HAND GESTURE RECOGNITION USING A SKELETON-BASED FEATURE REPRESENTATION WITH A RANDOM REGRESSION FOREST
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose a method for automatic hand gesture recognition using a random regression forest with a novel set of feature descriptors created from skeletal data acquired from the Leap Motion Controller. The efficacy of our proposed approach is evaluated on the publicly available University of Padova Microsoft Kinect and Leap Motion dataset, as well as 24 letters of the English alphabet in American Sign Language. The letters that are dynamic (e.g. j and z) are not evaluated.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views- Read more about Combining Gaze and Demographic Feature Desciptors for Autism Classification
- Log in to post comments
People with autism suffer from social challenges and communication difficulties, which may prevent them from leading a fruitful and enjoyable life. It is imperative to diagnose and start treatments for autism as early as possible and, in order to do so, accurate methods of identifying the disorder are vital. We propose a novel method for classifying autism through the use of eye gaze and demographic feature descriptors that include a subject’s age and gender. We construct feature descriptors that incorporate the subject’s age and gender, as well as features based on eye gaze data.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views- Read more about Presentation Slides for paper #3118
- Log in to post comments
Gradient control plays an important role in feed-forward networks applied to various computer vision tasks. Previous work has shown that Recurrent Highway Networks minimize the problem of vanishing or exploding gradients. They achieve this by setting the eigenvalues of the temporal Jacobian to 1 across the time steps. In this work, batch normalized recurrent highway networks are proposed to control the gradient flow in an improved way for network convergence. Specifically, the introduced model can be formed by batch normalizing the inputs at each recurrence loop.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views- Read more about Adaptive thresholding HOSVD algorithm with iterative regularization for image denoising
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views- Read more about Adaptive thresholding HOSVD algorithm with iterative regularization for image denoising
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 ViewsIn many real life application measured data takes its values on Riemannian manifolds. For the special case of the Euclidean space this setting includes the classical grayscale and color images. Like these classical images, manifold-valued data might suffer from measurement errors in form of noise or missing data. In this paper we present the manifold-valued image restoration toolbox (MVIRT) that provides implementations of classical image processing tasks.
- Categories:
 129 Views
129 Views