- Read more about A Linear Regression Framework For Assessing Time-Varying Subjective Quality in HTTP Streaming
- Log in to post comments
In an HTTP streaming framework, continuous time quality evaluation is necessary to monitor the time-varying subjective quality (TVSQ) of the videos resulting from rate adaptation. In this paper, we present a novel learning framework for TVSQ assessment using linear regression under the Reduced-Reference (RR) and the No-Reference (NR) settings. The proposed framework relies on objective short time quality estimates and past TVSQs for predicting the present TVSQ.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views- Read more about Efficient Segmentation-Aided Text Detection for Intelligent Robots_Poster
- Log in to post comments
Scene text detection is a critical prerequisite for many fascinating applications for vision-based intelligent robots. Existing methods detect texts either using the local information only or casting it as a semantic segmentation problem. They tend to produce a large number of false alarms or cannot separate individual words accurately. In this work, we present an elegant segmentation-aided text detection solution that predicts the word-level bounding boxes using an end-to-end trainable deep convolutional neural network.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about FAST NEAR INFRARED FUSION-BASED ADAPTIVE ENHANCEMENT OF VISIBLE
- Log in to post comments
Visible (VS) and near infra-red (NIR) band sensors provide digital
images that capture complementary spectral radiations from a
scene. Since NIR radiations propagate well through haze, mist, or
fog, the captured NIR image contains better scene details compared
to the VS image in such cases. However, NIR radiations are material
dependent and provide little information about color or texture of
the scene’s objects. To exploit the complementary details provided
by VS and NIR images, we propose a fusion approach that adaptively
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views- Read more about FAST NEAR INFRARED FUSION-BASED ADAPTIVE ENHANCEMENT OF VISIBLE
- Log in to post comments
Visible (VS) and near infra-red (NIR) band sensors provide digital
images that capture complementary spectral radiations from a
scene. Since NIR radiations propagate well through haze, mist, or
fog, the captured NIR image contains better scene details compared
to the VS image in such cases. However, NIR radiations are material
dependent and provide little information about color or texture of
the scene’s objects. To exploit the complementary details provided
by VS and NIR images, we propose a fusion approach that adaptively
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views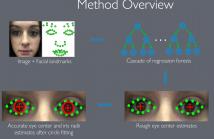
- Read more about Hybrid eye center localization using cascaded regression and robust circle fitting
- Log in to post comments
We propose a new cascaded regressor for eye center detection. Previous methods start from a face or an eye detector and use either advanced features or powerful regressors for eye center localization, but not both. Instead, we detect the eyes more accurately using an existing facial feature alignment method. We improve the robustness of localization by using both advanced features and powerful regression machinery. Finally, unlike most other methods that do not refine the regression results, we make the localization more accurate by adding a robust circle fitting post-processing step.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views- Read more about SUPER-RESOLUTION FOR 2K/8K TELEVISION USING WAVELET-BASED IMAGE REGISTRATION
- Log in to post comments
We propose a super-resolution method to convert spatial resolution from 2K to 8K to utilize existing 2K HDTV video for 8K UHDTV broadcasting. The proposed method uses image registration for wavelet multi-scale bands of 2K video frames considering future hardware implementation to real-time processing. This image registration consists of alignment and assignment procedures. The wavelet multi-scale bands are extracted using wavelet decomposition of 2K video frames. The alignment is processed from 2K video frames to its wavelet low-frequency bands.
poster_pdf.pdf
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
An efficient video dehazing system based on the dark channel prior (DCP) is proposed. For the proposed system, the original DCP-based dehazing method is modified in order to achieve a fast execution of the airlight estimation without noticeable degradation of the dehazing quality. The proposed system is implemented in a heterogeneous multi-processor system-on-chip, for which the overall dehazing process is described in OpenCL and synthesized into the custom circuitry targeting an FPGA.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views- Read more about CNN ORIENTED FAST PU MODE DECISION FOR HEVC HARDWIRED INTRA ENCODER
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 41 Views
41 Views- Read more about Fast Fractional-Pixel Motion Estimation using Lagrangian-Based Error Surface Interpolation
- Log in to post comments
Motion Estimation is an important module in the HEVC encoder.
It is divided into Integer-pixel Motion Estimation followed
by Fractional-pixel motion Estimation for coding efficiency
improvement. In this paper, a new algorithm is proposed
to estimate the best fractional-pixel motion vector. It
is based on a mathematical model using the matching error
costs of the integer pixel locations around the best integer
candidate. The proposed algorithm is implemented in HEVC
standard software (HM-16.9). The experimental results show
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views- Read more about HIGHLY PARALLEL HEVC MOTION ESTIMATION BASED ON MULTIPLE TEMPORAL PREDICTORS AND NESTED DIAMOND SEARCH
- 3 comments
- Log in to post comments
Rate-constrained motion estimation (RCME) is the most computationally intensive task of H.265/HEVC encoding. Massively parallel architectures, such as graphics processing units (GPUs), used in combination with a multi-core central processing unit (CPU), provide a promising computing platform to achieve fast encoding. However, the dependencies in deriving motion vector predictors (MVPs) prevent the parallelization of prediction units (PUs) processing at a frame level.
- Categories:
 51 Views
51 Views