
- Read more about CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORKS AND MULTITASK STRATEGIES FOR SEMANTIC MAPPING OF NATURAL LANGUAGE INPUT TO A STRUCTURED DATABASE
- Log in to post comments
In this work, we investigate mapping both natural language food and quantity descriptions to matching USDA database entries. We demonstrate that a convolutional neural network (CNN) model with a softmax layer on top to directly predict the most likely database matches outperforms our previous state-of-the-art approach of learning binary classification and subsequently ranking database entries using similarity scores with the learned embeddings.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views- Read more about End-to-End Joint Learning of Natural Language Understanding and Dialogue Manager
- Log in to post comments
Natural language understanding and dialogue policy learning are both essential in conversational systems that predict the
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views- Read more about Dialog State Tracking and Action Selection Using Deep Learning Mechanism for Interview Coaching
- Log in to post comments
The best way to prepare for an interview is to review the different types of possible interview questions you will be asked during an interview and practice responding to questions. An interview coaching system tries to simulate an interviewer to provide mock interview practice simulation sessions for the users. The traditional interview coaching systems provide some feedbacks, including facial preference, head nodding, response time, speaking rate, and volume, to let users know their own performance in the mock interview.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views
- Read more about Evaluation of a Multimodal 3-D Pronunciation Tutor for Learning Mandarin as a Second Language:An Eye-tracking Study
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 ViewsThe paper proposed a method to realize a speech-to-gesture conversion for communication between normal and speech-impaired people. Keyword spotting was employed to recognize the keywords from input speech signals. At the same time, the three dimensional gesture models of keywords were built by 3D modeling technology according to the "Chinese sign language". The speech-to-gesture conversion was finally realized by playing the corresponding 3D gestures with OpenGL from the results of keyword spotting.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views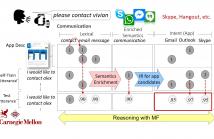
- Read more about Poster for Unsupervised User Intent Modeling by Feature-Enriched Matrix Factorization
- Log in to post comments
Spoken language interfaces are being incorporated into various devices such as smart phones and TVs. However, dialogue systems may fail to respond correctly when users’ request functionality is not supported by currently installed apps. This paper proposes a feature-enriched matrix factorization (MF) approach to model open domain intents, which allows a system to dynamically add unexplored domains according to users’ requests.
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views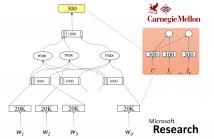
- Read more about Poster for Zero-Shot Learning of Intent Embeddings for Expansion by Convolutional Deep Structured Semantic Models
- Log in to post comments
The recent surge of intelligent personal assistants motivates spoken language understanding of dialogue systems. However, the domain constraint along with the inflexible intent schema remains a big issue. This paper focuses on the task of intent expansion, which helps remove the domain limit and make an intent schema flexible. A convolutional deep structured semantic model (CDSSM) is applied to jointly learn the representations for human intents and associated utterances.
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views