
- Read more about MULTI-STAGE RESIDUAL HIDING FOR IMAGE-INTO-AUDIO STEGANOGRAPHY
- Log in to post comments
The widespread application of audio communication technologies has speeded up audio data flowing across the Internet, which made it an popular carrier for covert communication. In this paper, we present a cross-modal steganography method for hiding image content into audio carriers while preserving the perceptual fidelity of the cover audio.
- Categories:
 132 Views
132 Views
- Read more about A New Spatial Steganographic Scheme by Modeling Image Residuals with Multivariate Gaussian Model
- Log in to post comments
Embedding costs used in content-adaptive image steganographic schemes can be defined in a heuristic way or with a statistical model. Inspired by previous steganographic methods, i.e., MG (multivariate Gaussian model) and MiPOD (minimizing the power of optimal detector), we propose a model-driven scheme in this paper. Firstly, we model image residuals obtained by high-pass filtering with quantized multivariate Gaussian distribution. Then, we derive the approximated Fisher Information (FI). We show that FI is related to both Gaussian variance and filter coefficients.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views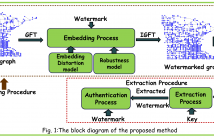
- Read more about Graph Spectral Domain Blind Watermarking
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes the first ever graph spectral domain blind watermarking algorithm. We explore the recently developed graph signal processing for spread-spectrum watermarking to authenticate the data recorded on non-Cartesian grids, such as sensor data, 3D point clouds, Lidar scans and mesh data. The choice of coefficients for embedding the watermark is driven by the model for minimisation embedding distortion and the robustness model.
- Categories:
 67 Views
67 Views
- Read more about MAXIMALLY SEPARATED AVERAGES PREDICTION FOR HIGH FIDELITY REVERSIBLE DATA HIDING
- Log in to post comments
Recently pixel pairing and pixel sorting/selection have been used in prediction-error expansion based reversible data hiding schemes to generate low entropy prediction-error histograms (PEH) necessary for achieving high fidelity. Such schemes generally use the four-neighbor average rhombus predictor as it allows pixel sorting and flexible pixel pairing. In this paper, we propose the maximally separated averages (MSA) predictor that uses the four-neighborhood context.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
Training deep neural networks is a computationally expensive task. Furthermore, models are often derived from proprietary datasets that have been carefully prepared and labelled. Hence, creators of deep learning models want to protect their models against intellectual property theft. However, this is not always possible, since the model may, e.g., be embedded in a mobile app for fast response times. As a countermeasure watermarks for deep neural networks have been developed that embed secret information into the model.
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views
- Read more about ICASSP 2019 Poster
- Log in to post comments
The method reported here realizes an inaudible echo-hiding based speech watermarking by using sparse subspace clustering (SSC). Speech signal is first analyzed with SSC to obtain its sparse and low-rank components. Watermarks are embedded as the echoes of the sparse component for robust extraction. Self-compensated echoes consisting of two independent echo kernels are designed to have similar delay offsets but opposite amplitudes. A one-bit watermark is embedded by separately performing the echo kernels on the sparse and low-rank components.
- Categories:
 58 Views
58 Views
- Read more about RHFCN: Fully CNN-based Steganalysis of MP3 with Rich High-Pass Filtering
- Log in to post comments
Recent studies have shown that convolutional neural networks (CNNs) can boost the performance of audio steganalysis. In this paper, we propose a well-designed fully CNN architecture for MP3 steganalysis based on rich high-pass filtering (HPF). On the one hand, multi-type HPFs are employed for "residual" extraction to enlarge the traces of the signal in view of the truth that signal introduced by secret messages can be seen as high-pass frequency noise.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 80 Views
80 Views
- Read more about UNIFORM EMBEDDING FOR EFFICIENT STEGANOGRAPHY OF H.264 VIDEO
- Log in to post comments
ICIP海报.pdf
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Read more about IMPROVED PAIRWISE PIXEL-VALUE-ORDERING FOR HIGH-FIDELITY REVERSIBLE DATA HIDING
- Log in to post comments
Pixel-value-ordering (PVO) appears as an efficient technique for high-fidelity reversible data hiding. This paper proposes a reversible data hiding scheme based on the pairwise PVO framework with improved difference equations. Both the pixel pair selection and the embedding algorithms are also streamlined. The proposed scheme uses a block classification approach based on a local complexity metric. Uniform blocks are processed using the proposed improved pairwise PVO algorithm. Slightly noisy blocks are embedded using a classic PVO scheme and noisy blocks are kept unchanged.
- Categories:
 65 Views
65 Views
- Read more about REVERSIBLE DATA HIDING IN ENCRYPTED COLOR IMAGES BASED ON VACATING ROOM AFTER ENCRYPTION AND PIXEL PREDICTION
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes a new vacating room after encryption reversible data hiding scheme developed for color images. The proposed scheme uses standard exclusive-or encryption and inherits the main features of vacating room after encryption schemes, namely joint and separate methods for data embedding. The proposed scheme exploits both the correlation between neighboring pixels and the correlation between color channels by predicting the original pixel values on color channel differences.
- Categories:
 53 Views
53 Views