
- Read more about SEMANTIC SEGMENTATION FOR MULTI-SCENE REMOTE SENSING IMAGES WITH NOISY LABELS BASED ON UNCERTAINTY PERCEPTION
- Log in to post comments
As the annotation of remote sensing images requires domain expertise, it is difficult to construct a large-scale and accurate annotated dataset. Image-level annotation data learning has become a research hotspot. In addition, due to the difficulty in avoiding mislabeling, label noise cleaning is also a concern. In this paper, a semantic segmentation method for remote sensing images based on uncertainty perception with noisy labels is proposed. The main contributions are three-fold.
- Categories:
 56 Views
56 Views
- Read more about HYPERPIXELS: FLEXIBLE 4D OVER-SEGMENTATION FOR DENSE AND SPARSE LIGHT FIELDS
- Log in to post comments
4D Light Field (LF) imaging, since it conveys both spatial and angular scene information, can facilitate computer vision tasks and generate immersive experiences for end-users.
A key challenge in 4D LF imaging is to flexibly and adaptively represent the included spatio-angular information to facilitate subsequent computer vision applications. Recently, image over-segmentation into homogenous regions with perceptually meaningful information has been exploited to represent 4D LFs. However, existing methods assume densely sampled LFs and
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about Building Lane-Level Maps from Aerial Images -
- Log in to post comments
Detecting lane lines from sensors is becoming an increasingly significant part of autonomous driving systems. However, less development has been made on high-definition lane-level mapping based on aerial images, which could automatically build and update offline maps for auto-driving systems. To this end, our work focuses on extracting fine-level detailed lane lines together with their topological structures. This task is challenging since it requires large amounts of data covering different lane types, terrain and regions.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about EXPLORATION OF VISUAL PROMPT IN GROUNDED PRE-TRAINED OPEN-SET DETECTION
- Log in to post comments
Text prompts are crucial for generalizing pre-trained open-set object detection models to new categories. However, current methods for text prompts are limited as they require manual feedback when generalizing to new categories, which restricts their ability to model complex scenes, often leading to incorrect detection results. To address this limitation, we propose a novel visual prompt method that learns new category knowledge from a few labeled images, which generalizes the pre-trained detection model to the new category.
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
- Read more about Contextual Human Object Interaction Understanding From Pre-Trained Large Language Model
- Log in to post comments
Existing human object interaction (HOI) detection methods have introduced zero-shot learning techniques to recognize unseen interactions, but they still have limitations in understanding context information and comprehensive reasoning. To overcome these limitations, we propose a novel HOI learning framework, ContextHOI, which serves as an effective contextual HOI detector to enhance contextual understanding and zero-shot reasoning ability. The main contributions of the proposed ContextHOI are a novel context-mining decoder and a powerful interaction reasoning large language model (LLM).
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views
- Read more about Highlight removal network based on an improved dichromatic reflection model
- Log in to post comments
State-of-the-art highlight removal methods still face the problems of color inconsistencies between highlight region and background, and content unreality in highlight areas.
To solve these two problems, we propose a novel adaptive highlight-aware network for specular highlight removal based on an improved dichromatic reflection model.
For color inconsistencies, we propose an adaptive highlight-aware (AHA) module to perceive the complete highlight information including the location and the scale of the specular highlight.
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views
- Read more about Neural Network Training Strategy to Enhance Anomaly Detection Performance: A Perspective on Reconstruction Loss Amplification
- Log in to post comments
Unsupervised anomaly detection (UAD) is a widely adopted approach in industry due to rare anomaly occurrences and data imbalance. A desirable characteristic of an UAD model is contained generalization ability which excels in the reconstruction of seen normal patterns but struggles with unseen anomalies. Recent studies have pursued to contain the generalization capability of their UAD models in reconstruction from different perspectives, such as design of neural network (NN) structure and training strategy.
- Categories:
 174 Views
174 Views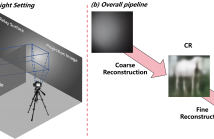
- Read more about PROGRESSIVE PASSIVE NON-LINE-OF-SIGHT IMAGING WITH LARGE MODEL PRIORS
- Log in to post comments
Passive non-line-of-sight (NLOS) imaging has developed rapidly in recent years. However, existing models generally suffer from low-quality reconstruction due to the severe loss of information during the projection process. This paper proposes a two-stage passive NLOS imaging approach, aimed at reconstructing high-quality complicated hidden scenes. In the first stage, we train a coarse reconstruction network based on the optimal transport principle and using vector quantization to learn discrete priors for projection image encoding.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views
- Read more about Supplementary Materials for "EXPLAINING 3D OBJECT DETECTION THROUGH SHAPLEY VALUE-BASED ATTRIBUTION MAP"
- Log in to post comments
Supplementary materials of ICIP 2024
Title: "EXPLAINING 3D OBJECT DETECTION THROUGH SHAPLEY VALUE-BASED ATTRIBUTION MAP"
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views
- Read more about SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL - SWISS: FLEXIBLE, UNIFIED WEAKLY-SUPERVISED INSTANCE SEGMENTATION UTILIZING FOUNDATION MODELS
- Log in to post comments
Supplementary material of ICIP 2024 submission SWISS: FLEXIBLE, UNIFIED WEAKLY-SUPERVISED INSTANCE SEGMENTATION UTILIZING FOUNDATION MODELS
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views