
- Read more about HIERARCHY-AWARE LOSS FUNCTION ON A TREE STRUCTURED LABEL SPACE FOR AUDIO EVENT DETECTION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views
- Read more about Modeling nonlinear audio effects with end-to-end deep neural networks
- Log in to post comments
Audio processors whose parameters are modified periodically
over time are often referred as time-varying or modulation based
audio effects. Most existing methods for modeling these type of
effect units are often optimized to a very specific circuit and cannot
be efficiently generalized to other time-varying effects. Based on
convolutional and recurrent neural networks, we propose a deep
learning architecture for generic black-box modeling of audio processors
with long-term memory. We explore the capabilities of
- Categories:
 53 Views
53 Views
- Read more about CNN Based Two-Stage Multi-Resolution End-to-End Model for Singing Melody Extraction
- Log in to post comments
Inspired by human hearing perception, we propose a twostage multi-resolution end-to-end model for singing melody extraction in this paper. The convolutional neural network (CNN) is the core of the proposed model to generate multiresolution representations. The 1-D and 2-D multi-resolution analysis on waveform and spectrogram-like graph are successively carried out by using 1-D and 2-D CNN kernels of different lengths and sizes.
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views
- Read more about Contextual Speech Recognition with Difficult Negative Training Examples
- Log in to post comments
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
- Read more about Exploring CTC-network derived features with conventional hybrid system
- Log in to post comments
icassp2018.pdf
- Categories:
 118 Views
118 Views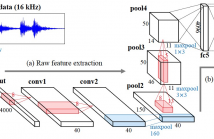
- Read more about Learning Environmental Sounds with End-to-end Convolutional Neural Network
- Log in to post comments
Environmental sound classification (ESC) is usually conducted based on handcrafted features such as the log-mel feature. Meanwhile, end-to-end classification systems perform feature extraction jointly with classification and have achieved success particularly in image classification. In the same manner, if environmental sounds could be directly learned from the raw waveforms, we would be able to extract a new feature effective for classification that could not have been designed by humans, and this new feature could improve the classification performance.
poster1.pdf
- Categories:
 49 Views
49 Views- Read more about Cluster-Based Senone Selection for the Efficient Calculation of Deep Neural Network Acoustic Models
- Log in to post comments
This is oral presentation at ISCSLP, for more information, please refer to paper:
Jun-Hua Liu, Zhen-Hua Ling, Si Wei, Guo-Ping Hu, Li-Rong Dai, "Cluster-Based Senone Selection for the Efficient Calculation of Deep Neural Network Acoustic Models", ISCSLP, 2016.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about Acoustic detection and localization of impulsive events in urban environments
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views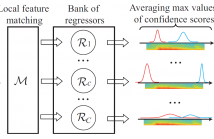
- Read more about LEARNING COMPACT STRUCTURAL REPRESENTATIONS FOR AUDIO EVENTS USING REGRESSOR BANKS
- Log in to post comments
We introduce a new learned descriptor for audio signals which is efficient for event representation. The entries of the descriptor are produced by evaluating a set of regressors on the input signal. The regressors are class-specific and trained using the random regression forests framework. Given an input signal, each regressor estimates the onset and offset positions of the target event. The estimation confidence scores output by a regressor are then used to quantify how the target event aligns with the temporal structure of the corresponding category.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views- Read more about Temporal Alignment for Deep Neural Networks
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views