
- Read more about A New Perspective on Randomized Gossip Algorithms
- Log in to post comments
In this short note we propose a new approach for the design and analysis of randomized gossip algorithms which can be used to solve the average consensus problem. We show how the Randomized Block Kaczmarz (RBK) method—a method for solving linear systems—works as gossip algorithm when applied to a special system encoding the underlying network. The famous pairwise gossip algorithm arises as a special case.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about A New Perspective on Randomized Gossip Algorithms
- Log in to post comments
In this short note we propose a new approach for the design and analysis of randomized gossip algorithms which can be used to solve the average consensus problem. We show how the Randomized Block Kaczmarz (RBK) method—a method for solving linear systems—works as gossip algorithm when applied to a special system encoding the underlying network. The famous pairwise gossip algorithm arises as a special case.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about Inter-cell Interference Coordination for Multi-color Visible Light Communication Networks
- Log in to post comments
We address the inter-cell interference coordination for the indoor multi-color visible light communication (VLC) network under lighting constraints. In the multi-color VLC system, soft frequency reuse-based interference coordination is adopted, which adjusts the AC powers of the cell-edge components and the cell-center components. To further improve the system throughput in the environment of dense LED deployment, we propose the dynamic scheduler for the inter-cell interference coordination.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about Achievable Rate and Optimal Signaling for an Optical Wireless Decode-and-Forward Relaying Channel
- Log in to post comments
This paper studies the achievable rate of a relay- assisted optical wireless communication channel, and presents a novel discrete signaling method by our proposed symbol-number filling algorithm. Unlike the radio frequency counterpart, the signaling is designed subject to nonnegative, peak and average power constraints, taking the input-dependent Gaussian shot noise into account. Decode and forward (DF) protocol is adopted by the relay, and is shown to outperform the direct transmission (DT) protocol.
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views
- Read more about ENERGY-EFFICIENT JOINT TRANSMIT BEAMFORMING AND SUBARRAY SELECTION WITH NON-LINEAR POWER AMPLIFIER EFFICIENCY
- Log in to post comments
We study the problem of energy efficiency maximization (EEmax) with joint beamforming and subarray selection, by taking into account the non-linear power amplifier efficiency in a multi-user multiple-input single-output system. The subarray selection problem is formulated using the concept of perspective formulation with additional penalty term in the objective function. To tackle the resulting challenging mixed-Boolean non-convex optimization problem, we rely on
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views
- Read more about Improved Decoding of Analog Modulo Block Codes for Noise Mitigation
- Log in to post comments
A drawback of digital transmission of analog signals is the unavoidable quantization error which leads to a limited quality even for good channel conditions.
This saturation can be avoided by using analog transmission systems with discrete-time and quasi-continuous-amplitude encoding and decoding, e.g., Analog Modulo Block codes (AMB codes). The AMB code vectors are produced by multiplying a real-valued information vector with a real-valued generator matrix using a modulo arithmetic.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views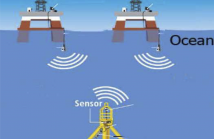
- Read more about RSS-BASED SENSOR LOCALIZATION IN UNDERWATER ACOUSTIC SENSOR NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
Since the global positioning system (GPS) is not applicable underwater, source localization using wireless sensor networks (WSNs) is gaining popularity in oceanographic applications. Unlike terrestrial WSNs (TWSNs) which use electromagnetic signaling, underwater WSNs (UWSNs) require underwater acoustic (UWA) signaling. Received signal strength (RSS)-based source localization is considered in this paper due to its practical simplicity and the constraint of low-cost sensor devices, but this area received little attention so far because of the complicated UWA transmission loss (TL) phenomena.
RSSmain.pdf
- Categories:
 55 Views
55 Views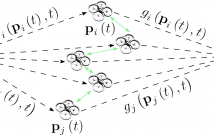
- Read more about Mobile Beamforming & Spatially Controlled Relay Communications
- Log in to post comments
We consider stochastic motion planning in single-source single-destination robotic relay networks, under a cooperative beamforming framework. Assuming that the communication medium constitutes a spatiotemporal stochastic field, we propose a
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views