- Watermarking and Steganography
- Signal Processing and Cryptography
- Multimedia Forensics
- Communications and Network Security
- Biometrics
- Applications

- Read more about Supplementary Material FaceLiVT ICCE-TW 25
- Log in to post comments
This supplementary material provides implementation specifics and extra quality comparisons to further illustrate FaceLiVT's effectiveness and superiority over existing approaches. With these additional evaluations, we aim to offer a thorough analysis and underscore the benefits of our approach.
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about Diffusion to Confusion Adversarial Patch
- Log in to post comments
Supplementary Materials
- Categories:
 42 Views
42 Views
- Read more about 1
- Log in to post comments
Improving Feature-level Adversarial Transferability via Diversity Attribution: Supplementary Materials for Papers Submitted to ICIP2025.
- Categories:
 133 Views
133 Views
- Read more about Open-Set deepfake detection to fight the unknown
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we design a new open-set method to detect deepfakes that does not assume information about the techniques behind the deepfakes generation. Contrary to existing methods, which build upon known telltales left by the deepfake creation process, we assume no prior knowledge about the sample generation, thus presenting a method for blind deepfake detection, a necessary step toward true generalization.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about DROPFL: Client Dropout Attacks Against Federated Learning Under Communication Constraints
- Log in to post comments
Federated learning (FL) has emerged as a promising paradigm for decentralized machine learning while preserving data privacy. However, under communication constraints, the standard FL protocol faces the risk of client dropout. Although some research has focused on the risk from the perspectives of communication optimization and privacy protection, it is still challenging to deal with the client dropout issue in dynamic networks, where clients may join or drop the training process at any time.
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views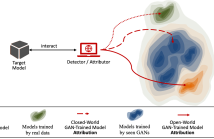
- Read more about Detection and Attribution of Models Trained on Generated Data
- Log in to post comments
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have become widely used in model training, as they can improve performance and/or protect sensitive information by generating data. However, this also raises potential risks, as malicious GANs may compromise or sabotage models by poisoning their training data. Therefore, it is important to verify the origin of a model’s training data for accountability purposes. In this work, we take the first step in the forensic analysis of models trained on GAN-generated data. Specifically, we first detect whether a model is trained on GAN-generated or real data.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views
In this paper, we develop a framework to achieve a desirable trade-off between fairness, inference accuracy and privacy protection in the inference as service scenario. Instead of sending raw data to the cloud, we conduct a random mapping of the data, which will increase privacy protection and mitigate bias but reduce inference accuracy. To properly address the trade-off, we formulate an optimization problem to find the optimal transformation map. As the problem is nonconvex in general, we develop an iterative algorithm to find the desired map.
poster_V1.pdf
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about Slides for SCALABLE PRIVACY-PRESERVING DISTRIBUTED EXTREMELY RANDOMIZED TREES FOR STRUCTURED DATA WITH MULTIPLE COLLUDING PARTIES
- Log in to post comments
Today, in many real-world applications of machine learning algorithms, the data is stored on multiple sources instead of at one central repository. In many such scenarios, due to privacy concerns and legal obligations, e.g., for medical data, and communication/computation overhead, for instance for large-scale data, the raw data cannot be transferred to a center for analysis. Therefore, new machine learning approaches are proposed for learning from the distributed data in such settings. In this paper, we extend the distributed Extremely Randomized Trees (ERT) approach w.r.t.
- Categories:
 40 Views
40 Views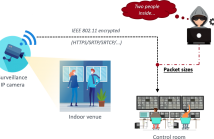
- Read more about Looking through Walls: Inferring Scenes from Video-Surveillance Encrypted Traffic
- Log in to post comments
Nowadays living environments are characterized by networks of inter-connected sensing devices that accomplish different tasks, e.g., video-surveillance of an environment by a network of CCTV cameras. A malicious user could gather sensitive details on people’s activities by eavesdropping the exchanged data packets. To overcome this problem,video streams are protected by encryption systems, but even secured channels may still leak some information.
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views