
- Read more about End-To-End Deep Learning-Based Adaptation Control for Frequency-Domain Adaptive System Identification
- Log in to post comments
We present a novel end-to-end deep learning-based adaptation control algorithm for frequency-domain adaptive system identification. The proposed method exploits a deep neural network to map observed signal features to corresponding step-sizes which control the filter adaptation. The parameters of the network are optimized in an end-to-end fashion by minimizing the average normalized system distance of the adaptive filter.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about Deep Residual Echo Suppression with a Tunable Tradeoff Between Signal Distortion and Echo Suppression
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose a residual echo suppression method using a UNet neural network that directly maps the outputs of a linear acoustic echo canceler to the desired signal in the spectral domain. This system embeds a design parameter that allows a tunable tradeoff between the desired-signal distortion and residual echo suppression in double-talk scenarios. The system employs 136 thousand parameters, and requires 1.6 Giga floating-point operations per second and 10 Mega-bytes of memory.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about Efficient Multichannel Nonlinear Acoustic Echo Cancellation Based On A Cooperative Strategy
- Log in to post comments
While a common approach to address nonlinear distortions, emitted by multiple loudspeakers and observed by multiple microphones, is to use post-filtering techniques, this paper proposes a cooperative strategy to rather model and then cancel such distortions. In this approach, the overall problem of modeling distortions emitted by a number of loudspeakers is divided into multiple simpler and easier tasks of estimating distortions emitted by subsets of loudspeakers.
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views
- Read more about A Recursive Least-Squares Algorithm Based on the Nearest Kronecker Product Decomposition
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about Efficient Nonlinear Acoustic Echo Cancellation by Dual-stage Multi-channel Kalman Filtering
- Log in to post comments
Mobile devices for hands-free speech communication often show significant nonlinear distortion in the sound emitted by their loudspeakers. Therefore, conventional linear echo cancellation is not sufficient for maintaining a high conversation quality. In this work we propose a nonlinear echo canceller that uses two serially cascaded adaptive filters to compensate for the nonlinear and linear echo. We show that a stable operation of the cascaded structure is achieved by using the multi-channel Kalman algorithm in the frequency domain with filtered-x references.
- Categories:
 102 Views
102 Views
- Read more about Multiple-input neural network-based residual echo suppression
- Log in to post comments
A residual echo suppressor (RES) aims to suppress the residual echo in the output of an acoustic echo canceler (AEC). Spectral-based RES approaches typically estimate the magnitude spectra of the near-end speech and the residual echo from a single input, that is either the far-end speech or the echo computed by the AEC, and derive the RES filter coefficients accordingly. These single inputs do not always suffice to discriminate the near-end speech from the remaining echo.
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 Views
- Read more about NONLINEAR ACOUSTIC ECHO CANCELLATION USING ELITIST RESAMPLING PARTICLE FILTER
- Log in to post comments
This paper considers an effective method for nonlinear acoustic echo cancellation (NL-AEC). More specifically, we model the nonlinear echo path by a latent state vector capturing the coefficients of a memoryless processor and a linear finite impulse response filter. To estimate the posterior probability distribution of the state vector, an elitist particle filter based on evolutionary strategies (EPFES) has been proposed, which evaluates realizations of the latent state vector based on long-term fitness measures.
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 Views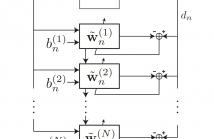
We introduce in this paper the recursive Hessian sketch, a new adaptive filtering algorithm based on sketching the same exponentially weighted least squares problem solved by the recursive least squares algorithm. The algorithm maintains a number of sketches of the inverse autocorrelation matrix and recursively updates them at random intervals. These are in turn used to update the unknown filter estimate. The complexity of the proposed algorithm compares favorably to that of recursive least squares.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views