
- Read more about LOW COST VARIABLE STEP-SIZE LMS WITH MAXIMUM SIMILARITY TO THE AFFINE PROJECTION ALGORITHM
- Log in to post comments
The LMS algorithm is widely employed in adaptive systems due to its robustness, simplicity, and reasonable performance. However, it is well known that this algorithm suffers from a slow convergence speed when dealing with colored reference signals. Numerous variants and alternative algorithms have been proposed to address this issue, though all of them entail an increase in computational cost. Among the proposed alternatives, the affine projection algorithm stands out. This algorithm has the peculiarity of starting from N data vectors of the reference signal.
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views
- Read more about An Efficient Beam-Sharing Algorithm for RIS-aided Simultaneous Wireless Information and Power Transfer Applications
- Log in to post comments
Simultaneous wireless information and power transfer (SWIPT) is a key technology for enabling future high-tech lifestyles by guaranteeing the perpetual operation of trillions of low-power IoT devices. Currently, reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) is a promising technology for achieving cost-effective and energy-efficient wireless technologies. In this paper, we propose an efficient beam-sharing algorithm for RIS-aided SWIPT systems.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about An Efficient Beam-Sharing Algorithm for RIS-aided Simultaneous Wireless Information and Power Transfer Applications
- Log in to post comments
Simultaneous wireless information and power transfer (SWIPT) is a key technology for enabling future high-tech lifestyles by guaranteeing the perpetual operation of trillions of low-power IoT devices. Currently, reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) is a promising technology for achieving cost-effective and energy-efficient wireless technologies. In this paper, we propose an efficient beam-sharing algorithm for RIS-aided SWIPT systems.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about Reducing the Communication and Computational Cost of Random Fourier Features Kernel LMS in Diffusion Networks
- Log in to post comments
Diffusion kernel algorithms are interesting tools for distributed nonlinear estimation. However, for the sake of feasibility, it is essential in practice to restrict their computational cost and the number of communications. In this paper, we propose a censoring algorithm for adaptive kernel diffusion networks based on random Fourier features that locally adapts the number of nodes censored according to the estimation error.
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views

The paper deals with the state estimation of nonlinear stochastic dynamic systems with special attention on a grid-based numerical solution to the Bayesian recursive relations, the point-mass filter (PMF).
In the paper, a novel functional decomposition of the transient density describing the system dynamics is proposed.
The decomposition is based on a non-negative matrix factorization and separates the density into functions of the future and current states.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views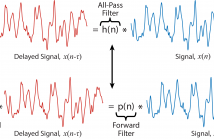
- Read more about An Adaptive All-Pass Filter for Time-Varying Delay Estimation
- Log in to post comments
The focus of this paper is the estimation of a delay between two signals. Such a problem is common in signal processing and particularly challenging when the delay is nonstationary in nature. Our proposed solution is based on an allpass filter framework comprising of two elements: a time delay is equivalent to all-pass filtering and an all-pass filter can be represented in terms of a ratio of a finite impulse response (FIR) filter and its time reversal.
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about SPARSE SUBSPACE TRACKING IN HIGH DIMENSIONS
- Log in to post comments
We studied the problem of sparse subspace tracking in the high-dimensional regime where the dimension is comparable to or much larger than the sample size. Leveraging power iteration and thresholding methods, a new provable algorithm called OPIT was derived for tracking the sparse principal subspace of data streams over time. We also presented a theoretical result on its convergence to verify its consistency in high dimensions. Several experiments were carried out on both synthetic and real data to demonstrate the effectiveness of OPIT.
- Categories:
 40 Views
40 Views
- Read more about Robust and efficient optimization scheme leading to KL transform
- Log in to post comments
In this paper we propose a novel and robust optimization scheme allowing to obtain the Karhunen-Lo`eve transform up to the permutation of row vectors. The introduced scheme is designed to be used in connection with artificial neural networks trained with the aid of gradient optimization techniques, and it involves two optimization criteria: (i) minimization of the mean squared error of signal reconstruction, (ii) minimization of the entropy related criterion.
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views