
Blind image deblurring (BID) is an ill-posed inverse problem, usually addressed by imposing prior knowledge on the (unknown) image and on the blurring filter. Most of the work on BID has focused on natural images, using image priors based on statistical properties of generic natural images. However, in many applications, it is known that the image being recovered belongs to some specific class (e.g., text, face, fingerprints), and exploiting this knowledge allows obtaining more accurate priors.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
Head pose estimation can help in understanding human behavior or to improve head pose invariance in various face analysis applications. Ready-to-use pose estimators are available with several facial landmark trackers, but their accuracy is commonly unknown. Following the goal to find the best landmark based pose estimator, we introduce a new database (called SyLaHP), propose a new benchmark protocol, and describe and implement a method to learn a pose estimator on top of any landmark detector (called HPFL).
Poster.pdf
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views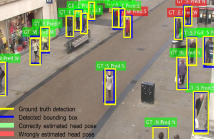
- Read more about Tiny Head Pose Classification by Bodily Cues
- Log in to post comments
The head pose is an important cue for computer vision. Traditionally considered in human computer interaction applications,
it becomes very hard to model in surveillance scenarios, due to the tiny head size. Additionally, no public dataset contains continuous head pose annotations in open scenery, making the challenge even harder to face. Here we present a
framework based on Faster RCNN, which introduces a branch in the network architecture related to the head pose estimation.
- Categories:
 239 Views
239 Views
Eyes represent the most distinctive features of the human face, while their position and movements are a significant source of information about the cognitive and affective state of humans. Precise eye center localization constitutes a challenging problem in many human-computer interaction applications. In this work, an automatic, non-intrusive method is introduced for the precise eye center localization,based on a modified version of the Fast Radial Symmetry Transform.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views
- Read more about Saliency Detection for Seismic Applications Using Multi-dimensional Spectral Projections and Directional Comparisons
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose a novel approach for saliency detection for seismic applications using 3D-FFT local spectra and multi-dimensional plane projections. We develop a projection scheme by dividing a 3D-FFT local spectrum of a data volume into three distinct components, each depicting changes along a different dimension of the data. The saliency detection results obtained using each projected component are then combined to yield a saliency map.
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views
- Read more about Saliency Detection for Seismic Applications Using Multi-dimensional Spectral Projections and Directional Comparisons
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose a novel approach for saliency detection for seismic applications using 3D-FFT local spectra and multi-dimensional plane projections. We develop a projection scheme by dividing a 3D-FFT local spectrum of a data volume into three distinct components, each depicting changes along a different dimension of the data. The saliency detection results obtained using each projected component are then combined to yield a saliency map.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 ViewsIn the past five years, salient object detection has become one of the hot topics in the field of computer vision. Focus is a naturally strong indicator for the salient object detection task, but is not well studied. A novel method is proposed in this paper to estimate the focus prior map for an arbitrary image. Different from the current edge density estimation based methods, the proposed method is based on the sparse defocus dictionary learning at a newly designed dataset. The focus strength is measured by the number of non-zero coefficients of the dictionary atoms.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views- Read more about FACIAL ANALYSIS IN THE WILD WITH LSTM NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 2 Views
2 Views- Read more about FACIAL ANALYSIS IN THE WILD WITH LSTM NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 ViewsCurrent object segmentation algorithms are based on the hypothesis that one has access to a very large amount of data. In this paper, we aim to segment objects using only tiny datasets. To this extent, we propose a new automatic part-based object segmentation algorithm for non-deformable and semi-deformable objects in natural backgrounds. We have developed a novel shape descriptor which models the local boundaries of an object's part. This shape descriptor is used in a bag-of-words approach for object detection.
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views