- Read more about WEAKLY SUPERVISED OBJECT LOCALIZATION WITH DEEP CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORK BASED ON SPATIAL PYRAMID SALIENCY MAP
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Read more about JOINT DEMOSAICING AND DENOISING OF NOISY BAYER IMAGES WITH ADMM
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 63 Views
63 Views
- Read more about JOINT WEBER-BASED ROTATION INVARIANT UNIFORM LOCAL TERNARY PATTERN FOR CLASSIFICATION OF PULMONARY EMPHYSEMA IN CT IMAGES
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we present a novel image representation approach for classifying emphysema in computed tomography (CT) images of the lung. Our proposed method extends rotation invariant uniform local binary pattern (RIULBP) and local ternary pattern (LTP), which are extensively used in a variety of computer vision applications, into rotation invariant uniform local ternary pattern (RIULTP) with a human perception principle: Weber’s law.
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views
- Read more about LUCKY DCT AGGREGATION FOR CAMERA SHAKE REMOVAL
- Log in to post comments
We consider the task of removing the effect of camera shake during a long exposure. Technically, this is a blind deconvolution problem in which both the image and the motion blur have to be jointly inferred. Several algorithms have been proposed till date for removing camera shake that work with one or more images. However, most of these algorithms are computationally expensive and hence cannot be used in real-time.
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views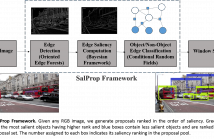
In this paper, we propose a novel object proposal generation scheme by formulating a graph-based salient edge classification framework that utilizes the edge context. In the proposed method, we construct a Bayesian probabilistic edge map to assign a saliency value to the edgelets by exploiting low level edge features. A Conditional Random Field is then learned to effectively combine these features for edge classification with object/non-object label. We propose an objectness score for the generated windows by analyzing the salient edge density inside the bounding box.
- Categories:
 164 Views
164 Views- Read more about MULTISPECTRAL FOCAL STACK ACQUISITION USING A CHROMATIC ABERRATION ENLARGED CAMERA
- Log in to post comments
Capturing more information, e.g. geometry and material, using optical cameras can greatly help the perception and understanding of complex scenes. This paper proposes a novel method to capture the spectral and light field information simultaneously. By using a delicately designed chromatic aberration enlarged camera, the spectral-varying slices at different depths of the scene can be easily captured.
icip oral.pdf
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views- Read more about Principal Noiseless Color Component Extraction by Linear Color Composition with Optimal Coefficients
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose a principal color component extraction
method that is simply performed by linear color composition (transformation)
of R, G, B colors, but its composite coefficients are calculated
so as to obtain a noisy-texture-less principal component of
RGB color images. Our method is related to principal component
analysis (PCA) and edge preserving smoothing by total variation
(TV) minimization. The resultant image becomes a principal color
component image with the minimum total variation. We show this
- Categories:
 1 Views
1 Views
- Read more about LOW COMPLEXITY IMAGE FUSION IN BAYER DOMAIN USING A MONOCHROME SENSOR AND BAYER SENSOR
- Log in to post comments
Mobile cameras have come a long way since their evolution and have replaced digital still cameras. However, their lowlight photography performance needs significant improvement. Dual camera systems consisting of a monochrome sensor and a Bayer sensor offer us a way to improve the low-light photography. The existing dual camera systems use post-processing methods after Image Signal Processor (ISP) for image fusion which are computationally intensive and use two ISPs. We propose a novel architecture in which the image fusion can be done in Bayer domain prior to the ISP.
- Categories:
 52 Views
52 Views
- Read more about Convolutional Gated Recurrent Networks for Video Segmentation
- Log in to post comments
Semantic segmentation has recently witnessed major progress, but most of the previous work focused on improving single image segmentation. In this paper, we introduce a novel approach to implicitly utilize temporal data in videos for online segmentation. This design receives a sequence of consecutive video frames and outputs the segmentation of the last frame. Convolutional gated recurrent networks are used for the recurrent part to preserve spatial connectivities in the image. This architecture is tested for both binary and semantic video segmentation tasks.
ICIP17.pdf
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views