- Read more about Noise-tolerant Deep Learning for Histopathological Image Segmentation
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 2 Views
2 Views- Read more about High Quality Reconstruction of Dynamic Objects using 2D-3D Camera Fusion
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about FLEXIBLE 3D NEIGHBORHOOD CASCADE DEFORMABLE PART MODELS FOR OBJECT DETECTION
- Log in to post comments
Cascade Deformable Part Models (DPMs) are cascade frameworks to speed up Deformable Part Models (DPMs), which are one of the state-of-the-art solutions for object detection. Its idea is to reject most non-object hypotheses from the early stages of detection process. By investigating the dependency between hypotheses over scales, we introduce a novel pruning method to accelerate Cascade DPM frameworks.
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views
- Read more about REAL-TIME WALKTHROUGH OF OUTDOOR SCENES USING TRI-VIEW MORPHING
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, an image-based walkthrough system is presented for navigating real-world outdoor scenes based on only three uncalibrated images without reconstructing 3D model. An image-based rendering operation is performed on these sample images and generates photorealistic in-between views in real time. We extend the traditional two-step view morphing to real-time tri-view morphing based on epipolar constraint.
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views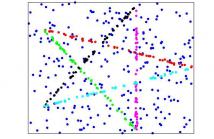
In this paper, we deal with geometric model fitting problems on graphs, where each vertex represents a model hypothesis,and each edge represents the similarity between two model hypotheses. Conventional median-shift methods are very efficient and they can automatically estimate the number of clusters. However, they assign the same weighting scores to all vertices of a graph, which can not show the discriminability on different vertices. Therefore, we propose a novel weighted median-shift on graphs method (WMSG) to fit and segment multiple-structure data.
ICIP_1400.pptx
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views- Read more about Face Recognition using Multi-modal Low-rank Dictionary Learning
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
ICIP_2570.pdf
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views- Read more about MULTI‐VIEW HUMAN ACTIVITY RECOGNITION USING MOTION FREQUENCY
- Log in to post comments
The problem of human activity recognition can be approached using spatio-temporal variations in successive video frames. In this paper, a new human action recognition technique is proposed using multi-view videos. Initially, a naive background subtraction using frame differencing between adjacent frames of a video is performed. Then, the motion information of each pixel is recorded in binary indicating existence/nonexistence of motion in the frame. A pixel wise sum over all the difference images in a view gives the frequency of motion in each pixel throughout the clip.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about Efficiently Building 3D Line Model with Points
- Log in to post comments
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 2 Views
2 Views
- Read more about Efficiently Building 3D Line Model with Points
- Log in to post comments
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views- Read more about HYPERLAPSE GENERATION OF OMNIDIRECTIONAL VIDEOS BY ADAPTIVE SAMPLING BASED ON 3D CAMERA POSITIONS
- Log in to post comments
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views