
- Read more about Semantic Understanding of Vision Transformer Representation Spaces for Enhanced Medical Image Classification
- Log in to post comments
In the last few years, vision transformers have increasingly been adopted for medical image classification and other applications due to their improved accuracies compared to other deep learning models. However, due to their size and complex interactions via the self-attention mechanism, they are not well understood. In particular, it is unclear whether the representations produced by such models are semantically meaningful.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about Highly Precise Motion Transitions Detection in Untrimmed Sports Videos Using Spatio-Temporal Graph Embeddings
- Log in to post comments
Fine-grained action localization in untrimmed sports videos is a challenging task, as motion transitions are subtle and occur within short time spans. Traditional supervised and weakly supervised methods require extensive labeled data, making them less scalable and generalizable. To address these challenges, we propose an unsupervised skeleton-based action localization pipeline that detects fine-grained action boundaries using spatio-temporal graph embeddings.
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views
- Read more about COT-AD: COTTON ANALYSIS DATASET
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents COT-AD, a comprehensive Dataset designed to enhance cotton crop analysis through computer vision. Comprising over 25,000 images captured throughout the cotton growth cycle, with 5,000 annotated images, COT-AD includes aerial imagery for field-scale detection and segmentation and high-resolution DSLR images documenting key diseases. The annotations cover pest and disease recognition, vegetation, and weed analysis, addressing a critical gap in cotton-specific agricultural datasets.
- Categories:
 40 Views
40 Views
- Read more about INVESTIGATING ROBUSTNESS OF UNSUPERVISED STYLEGAN IMAGE RESTORATION
- Log in to post comments
Recently, generative priors have shown significant improvement for unsupervised image restoration. This study explores the incorporation of multiple loss functions that capture various perceptual and structural aspects of image quality. Our proposed method improves robustness across multiple tasks, including denoising, upsampling, inpainting, and deartifacting, by utilizing a comprehensive loss function based on Learned Perceptual Image Patch Similarity(LPIPS), Multi-Scale Structural Similarity Index Measure Loss(MS-SSIM), Consistency, Feature, and Gradient losses.
- Categories:
 31 Views
31 Views

This document contains the supplementary material for the ICIP 2024 Paper with ID #2494 and Title "An End-to-End Class-Aware and Attention-Guided Model \\ for Object State Classification".
- Categories:
 35 Views
35 Views
- Read more about Supplementary Materials
- Log in to post comments
Supplementary materials for the paper on REBIS.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views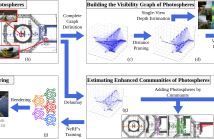
- Read more about Place-NeRFs
- Log in to post comments
We present the Place-NeRFs, a scalable approach to large-scale 3D scene reconstruction that subdivides scenes into non-overlapping regions that can be handled by off-the-shelf NeRF models, striking a balance between reconstruction quality and efficient use of computational resources. By leveraging rough single-view depth estimation and visibility graphs, Place-NeRFs effectively groups spatially correlated photospheres, enabling independent volumetric reconstructions. This approach significantly reduces processing time and enhances scalability during NeRF models' training.
- Categories:
 63 Views
63 Views
- Read more about Supplementary Material for Effective relationship between characteristics of training data and learning progress on knowledge distillation
- Log in to post comments
In image recognition, knowledge distillation is a valuable approach to train a compact model with high accuracy by exploiting outputs of a highly accurate large model as correct labels. In knowledge distillation, studies have shown the usefulness of data with high entropy output generated by image mix data augmentation techniques. Other strategies such as curriculum learning have also been proposed to improve model generalization by the control of the difficulty of training data over the learning process.
- Categories:
 63 Views
63 Views
- Read more about SUPPLEMENT FOR BIDIRECTIONAL FLOW FIELDS FOR SPARSE INPUT NOVEL VIEW SYNTHESIS OF DYNAMIC SCENES
- Log in to post comments
Supplemental material
- Categories:
 51 Views
51 Views