
- Read more about Privacy Preserving Federated Learning from Multi-input Functional Proxy Re-encryption
- Log in to post comments
Federated learning (FL) allows different participants to collaborate on model training without transmitting raw data, thereby protecting user data privacy. However, FL faces a series of security and privacy issues (e.g. the leakage of raw data from publicly shared parameters). Several privacy protection technologies, such as homomorphic encryption, differential privacy and functional encryption, are introduced for privacy enhancement in FL. Among them, the FL frameworks based on functional encryption better balance security and performance, thus receiving increasing attention.
- Categories:
 38 Views
38 Views
- Read more about Poster for IMAGE ATTRIBUTION BY GENERATING IMAGES
- Log in to post comments
We introduce GPNN-CAM, a novel method for CNN explanation, that bridges two distinct areas of computer vision:
Image Attribution, which aims to explain a predictor by highlighting image regions it finds important, and Single
Image Generation (SIG), that focuses on learning how to generate variations of a single sample. GPNN-CAM leverages samples generated by Generative
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views
- Read more about A UNIFIED DNN-BASED SYSTEM FOR INDUSTRIAL PIPELINE SEGMENTATION
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents a unified system tailored for autonomous pipe segmentation within an industrial setting. To this end, it is designed to analyze RGB images captured by Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV)-mounted cameras to predict binary pipe segmentation maps.
- Categories:
 38 Views
38 Views
- Read more about AUDIO-VISUAL SPEECH RECOGNITION IN-THE-WILD: MULTI-ANGLE VEHICLE CABIN CORPUS AND ATTENTION-BASED METHOD
- Log in to post comments
Audio-Visual Speech Recognition In-The-Wild: Multi-Angle Vehicle Cabin Corpus And Attention-Based Method
- Categories:
 37 Views
37 Views
- Read more about Lightning Talk- Situation-Aware Tranmit Beamforming for Automotive radar
- Log in to post comments
Millimeter-wave radar is a common sensor modality used in automotive driving for target detection and perception. These radars can benefit from side information on the environment being sensed, such as lane topologies or data from other sensors. Existing radars do not leverage this information to adapt waveforms or perform prior-aware inference. In this paper, we model the side information as an occupancy map and design transmit beamformers that are customized to the map. Our method maximizes the probability of detection in regions with a higher uncertainty on the presence of a target.
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about DISCOVERING MALICIOUS SIGNATURES IN SOFTWARE FROM STRUCTURAL INTERACTIONS
- Log in to post comments
Malware represents a significant security concern in today's digital landscape, as it can destroy or disable operating systems, steal sensitive user information, and occupy valuable disk space.
However, current malware detection methods, such as static-based and dynamic-based approaches, struggle to identify newly developed (``zero-day") malware and are limited by customized virtual machine (VM) environments.
To overcome these limitations, we propose a novel malware detection approach that leverages deep learning, mathematical techniques, and network science.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about MLPs Compass: What is Learned When MLPs are Combined with PLMs?
- Log in to post comments
While Transformer-based pre-trained language models and their variants exhibit strong semantic representation capabilities, the question of comprehending the information gain derived from the additional components of PLMs remains an open question in this field. Motivated by recent efforts that prove Multilayer-Perceptrons (MLPs) modules achieving robust structural capture capabilities, even outperforming Graph Neural Networks (GNNs), this paper aims to quantify whether simple MLPs can further enhance the already potent ability of PLMs to capture linguistic information.
poster-MLP.pdf
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views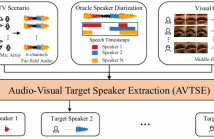
- Read more about THE MULTIMODAL INFORMATION BASED SPEECH PROCESSING (MISP) 2023 CHALLENGE: AUDIO-VISUAL TARGET SPEAKER EXTRACTION
- Log in to post comments
Previous Multimodal Information based Speech Processing (MISP) challenges mainly focused on audio-visual speech recognition (AVSR) with commendable success. However, the most advanced back-end recognition systems often hit performance limits due to the complex acoustic environments. This has prompted a shift in focus towards the Audio-Visual Target Speaker Extraction (AVTSE) task for the MISP 2023 challenge in ICASSP 2024 Signal Processing Grand Challenges.
misp2023ppt.pptx
- Categories:
 60 Views
60 Views
- Read more about MULTIMODAL SENTIMENT ANALYSIS BASED ON 3D STEREOSCOPIC ATTENTION
- Log in to post comments
In the multimodal (text, audio, and visual) sentiment analysis, the current methods generally consider the bi-modal sentiment interaction, resulting in inadequate mining and fusion of relations between modalities. In this paper, we propose the concept of multimodal 3D (3-Dimensional) stereoscopic attention for the first time, which constructs the tri-modal stereoscopic attention with temporal sequences simultaneously to adequately structure the sentiment interaction.
psoter.pdf
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about Counting Network for Learning from Majority Label
- Log in to post comments
The paper proposes a novel problem in multi-class Multiple-Instance Learning (MIL) called Learning from the Majority Label (LML). In LML, the majority class of instances in a bag is assigned as the bag's label. LML aims to classify instances using bag-level majority classes. This problem is valuable in various applications. Existing MIL methods are unsuitable for LML due to aggregating confidences, which may lead to inconsistency between the bag-level label and the label obtained by counting the number of instances for each class.
- Categories:
 47 Views
47 Views