
- Read more about PROMPTING AUDIOS USING ACOUSTIC PROPERTIES FOR EMOTION REPRESENTATION
- Log in to post comments
Emotions lie on a continuum, but current models treat emotions
as a finite valued discrete variable. This representation does not
capture the diversity in the expression of emotion. To better rep-
resent emotions we propose the use of natural language descrip-
tions (or prompts). In this work, we address the challenge of au-
tomatically generating these prompts and training a model to better
learn emotion representations from audio and prompt pairs. We use
acoustic properties that are correlated to emotion like pitch, intensity,
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views
- Read more about FOVEA TRANSFORMER: EFFICIENT LONG-CONTEXT MODELING WITH STRUCTURED FINE-TO-COARSE ATTENTION
- Log in to post comments
The quadratic complexity of self-attention in Transformers has hindered the processing of long text. To alleviate this problem, previous works have proposed to sparsify the attention matrix, taking advantage of the observation that crucial information about a token can be derived from its neighbors. These methods typically combine one or another form of local attention and global attention. Such combinations introduce abrupt changes in contextual granularity when going from local to global, which may be undesirable.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about NEW INTENT DISCOVERY WITH MULTI-VIEW CLUSTERING
- Log in to post comments
New intent discovery aims to identify new intents from unlabeled utterances in the open-world scenario. As the fundamental and challenging problem in dialogue systems, new intent discovery attracts increasing attention but is still under exploration. In this paper, we propose a simple and effective new intent discovery framework with multi-view clustering. Specifically, we first adopt a double-branch representation learning strategy to learn high-quality utterance representations.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about Neural Ordinary differential equations with Trainable solvers
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
When considering the data-driven identification of non-linear differential equations, the choice of the integration scheme to use is far from being trivial and may dramatically impact the identification problem. In this work, we discuss this aspect and propose a novel architecture that jointly learns Neural Ordinary Differential Equations (NODEs) as well as the corresponding integration schemes that would minimize the forecast of a given sequence of observations. We demonstrate its relevance with numerical experiments on non-linear dynamics, including chaotic systems.
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
- Read more about CAN LLM FIND THE GREEN CIRCLE? INVESTIGATION AND HUMAN-GUIDED TOOL MANIPULATION FOR COMPOSITIONAL GENERALIZATION
- Log in to post comments
The meaning of complex phrases in natural language is composed of their individual components. The task of compositional generalization evaluates a model's ability to understand new combinations of components. Previous studies trained smaller, task-specific models, which exhibited poor generalization. While large language models (LLMs) exhibit impressive generalization abilities on many tasks through in-context learning (ICL), their potential for compositional generalization remains unexplored.
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views
- Read more about BOOSTING ZERO-SHOT NODE CLASSIFICATION VIA DEPENDENCY CAPTURE AND DISCRIMINATIVE FEATURE LEARNING
- Log in to post comments
Zero-shot node classification aims to predict nodes belonging to novel classes that have not been seen in the training. Existing studies focus on transferring knowledge from seen classes to unseen classes, which have achieved good performance in most cases. However, they do not fully leverage the relationships between nodes and overlook the issue of domain bias, affecting overall performance. In this paper, we propose a novel dependency capture and discriminative feature learning (DCDFL) model for zero-shot node classification.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about Image Mixing and Gradient Smoothing to Enhance the SAR Image Attack
- Log in to post comments
Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) are known to be vulnerable to adversarial examples, which are crafted by adding imperceptible perturbations to clean examples. With the wide applications of DNNs to Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Automatic Target Recognition (ATR), the vulnerability of SAR deep recognition models has attracted increasing attention.
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about RADAR PERCEPTION WITH SCALABLE CONNECTIVE TEMPORAL RELATIONS FOR AUTONOMOUS DRIVING
- Log in to post comments
Due to the noise and low spatial resolution in automotive radar data, exploring temporal relations of learnable features over consecutive 2 radar frames has shown performance gain on downstream tasks (e.g., object detection and tracking) in our previous study. In this paper, we further enhance radar perception by significantly extending the time horizon of temporal relations.
- Categories:
 48 Views
48 Views
- Read more about EC-NAS: Energy Consumption Aware Tabular Benchmarks for Neural Architecture Search
- Log in to post comments
Energy consumption from the selection, training, and deployment of deep learning models has seen a significant uptick recently. This work aims to facilitate the design of energy-efficient deep learning models that require less computational resources and prioritize environmental sustainability by focusing on the energy consumption. Neural architecture search (NAS) benefits from tabular benchmarks, which evaluate NAS strategies cost-effectively through precomputed performance statistics. We advocate for including energy efficiency as an additional performance criterion in NAS.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views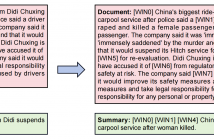
- Read more about Alleviating Hallucinations via Supportive Window Indexing in Abstractive Summarization
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Abstractive summarization models learned with maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) have been proven to produce hallucinatory content, which heavily limits their real-world
applicability. Preceding studies attribute this problem to the semantic insensitivity of MLE, and they compensate for it with additional unsupervised learning objectives that maximize the metrics of document-summary inferring, however, resulting in unstable and expensive model training. In this paper, we propose a novel supportive windows indexing
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views