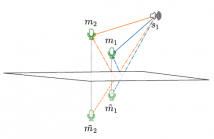
- Read more about MIRAGE: 2D sound source localization using microphone pair augmentation with echoes
- Log in to post comments
It is commonly observed that acoustic echoes hurt perfor-mance of sound source localization (SSL) methods. We in-troduce the concept of microphone array augmentation withechoes (MIRAGE) and show how estimation of early-echocharacteristics can in fact benefit SSL. We propose a learning-based scheme for echo estimation combined with a physics-based scheme for echo aggregation.
- Categories:
 150 Views
150 Views
- Read more about SOUND SOURCE LOCALIZATION IN A REVERBERANT ROOM USING HARMONIC BASED MUSIC
- Log in to post comments
The localization of acoustic sound sources is beneficial to signal processing applications of speech enhancement, dereverberation, separation and tracking. Difficulties in position estimation arise in real world environments due to coherent reflections degrading performance of subspace localization techniques. This paper proposes a method of multiple signal classification (MUSIC) subspace localization, which is suitable for reverberant rooms. The method is based on the modal decomposition of a room's region-to-region transfer function, which is assumed to be known.
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 Views- Read more about Joint Estimation of the Room Geometry and Modes with Compressed Sensing
- Log in to post comments
Acoustical behavior of a room for a given position of microphone and sound source is usually described using the room impulse response. If we rely on the standard uniform sampling, the estimation of room impulse response for arbitrary positions in the room requires a large number of measurements. In order to lower the required sampling rate, some solutions have emerged that exploit the sparse representation of the room wavefield in the terms of plane waves in the low-frequency domain. The plane wave representation has a simple form in rectangular rooms.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views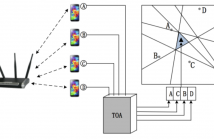
- Read more about ROBUST SEQUENCE-BASED LOCALIZATION IN ACOUSTIC SENSOR NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
Acoustic source localization in sensor network is a challenging task because of severe constraints on cost, energy, and effective range of sensor devices. To overcome these limitations in existing solutions, this paper formally describes, designs, implements, and evaluates a Half Plane Intersection method to Sequence-Based Localization, i.e., HPI-SBL, in distributed smartphone networks. The localization space can be divided into distinct regions, and each region can be uniquely identified by the node sequence that represents the ranking of distances from the reference nodes to the region.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about Speech Dereverberation Based on Integrated Deep and Ensemble Learning Algorithm
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about Improved Noise Characterization for Relative Impulse Response Estimation
- Log in to post comments
Relative Impulse Responses (ReIRs) have several applications in speech enhancement, noise suppression and source localization for multi-channel speech processing in reverberant environments. Noise is usually assumed to be white Gaussian during the estimation of the ReIR between two microphones. We show that the noise in this system identification problem is instead dependent upon the microphone measurements and the ReIR itself.
ICASSP_V3.pdf
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
- Read more about INFRASONIC SCENE FINGERPRINTING FOR AUTHENTICATING SPEAKER LOCATION
- Log in to post comments
Ambient infrasound with frequency ranges well below 20 Hz is known to carry robust navigation cues that can be exploited to authenticate the location of a speaker. Unfortunately, many of the mobile devices like smartphones have been optimized to work in the human auditory range, thereby suppressing information in the infrasonic region. In this paper, we show that these ultra-low frequency cues can still be extracted from a standard smartphone recording by using acceleration-based cepstral features.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views- Read more about CONFIDENCE MEASURES FOR CTC-BASED PHONE SYNCHRONOUS DECODING
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 41 Views
41 Views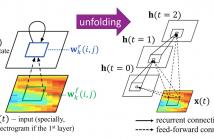
- Read more about RECURRENT CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORK FOR SPEECH PROCESSING
- Log in to post comments
Different neural networks have exhibited excellent performance on various speech processing tasks, and they usually have specific advantages and disadvantages. We propose to use a recently developed deep learning model, recurrent convolutional neural network (RCNN), for speech processing, which inherits some merits of recurrent neural network (RNN) and convolutional neural network (CNN). The core module can be viewed as a convolutional layer embedded with an RNN, which enables the model to capture both temporal and frequency dependence in the spectrogram of the speech in an efficient way.
- Categories:
 37 Views
37 Views