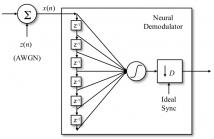
- Read more about EDUQA : EDUCATIONAL DOMAIN QUESTION ANSWERING SYSTEM USING CONCEPTUAL NETWORK MAPPING
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 46 Views
46 Views
- Read more about SMART DSP FOR A SMARTER POWER GRID: TEACHING POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS THROUGH SIGNAL PROCESSING
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 37 Views
37 Views
- Read more about Signals and Systems:Casting it as an Action-Adventure rather than a Horror Genre
- Log in to post comments
Simple but effective strategies for an undergraduate introductory course in signals and systems are described in this paper. These include peer facilitated tutorials, optional class tests, in-class only lab assessment and use of interactive animations. Peer facilitated tutorials were designed to support students to help other students. The optional class tests removed the stress and anxiety students face. With in-class only lab assessment the time students spent writing lab reports was replaced with time devoted to preparing and doing the lab together as a group.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views- Read more about ONLINE EDUCATION EVALUATION FOR SIGNAL PROCESSING COURSE THROUGH STUDENT LEARNING PATHWAYS
- Log in to post comments
Impact of online learning sequences to forecast course outcomes for an undergraduate digital signal processing (DSP) course is studied in this work. A multi-modal learning schema based on deep-learning techniques with learning sequences, psychometric measures, and personality traits as input features is developed in this work. The aim is to identify any underlying patterns in the learning sequences and subsequently forecast the learning outcomes.
icassp_v3.pptx
- Categories:
 132 Views
132 Views
Project-based learning is a form of active learning where large-scale projects provide context for technical learning. Along with background information, this paper examines teaching and learning of signals and systems in the context of two ABET accredited project-based learning programs. Examples of projects, deep learning activities and classroom activities are provided.
- Categories:
 219 Views
219 Views- Read more about Automatically Linking Digital Signal Processing Assessment Questions to Key Engineering Learning Outcomes
- Log in to post comments
To deliver on the potential outcome-based teaching and learning holds for engineering education, it is important for engineering courses to provide students with different types of deliberate practice opportunities that align to the program’s learning outcomes. Working from these requirements, we increased the design and measurement intentionality of a digital signal processing (DSP) course.
- Categories:
 117 Views
117 Views
- Read more about PROJECT HANDOVER IN UNDERGRADUATE PROJECTS – EFFICIENT HANDOVER FOR INCREASED LEARNING OPPORTUNITIES
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we describe a method we have employed at the University of Bristol to improve the undergraduate project experience. We describe the methodology we employ, which consists of a pre-built environment, close supervision by a researcher, and compiled reference material. We then compare the methodology with its absence using the frequency of undergraduates publishing as our metric. We observe a noticeable increase in the number of undergraduate publications under the new methodology, as well as a number of unexpected benefits for the students.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about HAND-RAISING GESTURE DETECTION IN REAL CLASSROOM
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 85 Views
85 Views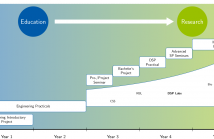
- Read more about Hands-on in Signal Processing Education at Technische Universität Darmstadt
- Log in to post comments
This paper is meant to share our experience on signal processing hands-on opportunities within the formal engineering education at Technische Universität Darmstadt. It is our strong belief that undergraduate students should be offered hands-on opportunities from the very beginning of their studies until their graduation. We describe our projects, lectures and seminars that we provide undergraduate students to gain hands-on experience inside signal processing along the time line of the curriculum.
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views