- Read more about Influence of Audio Bandwidth Reduction on Speech Emotion Recognition by Human Subjects
- Log in to post comments
Audio bandwidth reduction is the very first processing step in any speech and audio coder. Its negative influence on perceived speech quality and intelligibility has been thoroughly studied and is therefore very well documented. This paper examines whether it also has an influence on speech emotion recognition by human subjects. Several standard telephony bandwidths, from fullband down to narrowband, are considered. Listening test results show that recognition accuracy decreases with audio bandwidth.
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views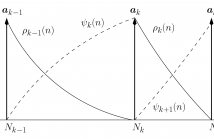
- Read more about NON-NEGATIVE TEMPORAL DECOMPOSITION REGULARIZATION WITH AN AUGMENTED LAGRANGIAN
- Log in to post comments
Nonnegative matrix factorization (NMF) has recently been applied to temporal decomposition (TD) of speech spectral envelopes represented by line spectral frequencies. A couple of inherent TD constraints, which are otherwise handled as ad hoc exceptions, has also been incorporated using NMF, including LSF ordering and monotonic event functions. Here, these constraints are analyzed and a third inherent constraint is incorporated into an NMF analysis.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views- Read more about System-Compatible Robustness Improvement for New Generation DECT Decoders by G.722 Soft-Decision Decoding
- Log in to post comments
The ITU-T Recommendation G.722 about subband adaptive differential pulse code modulation (SB-ADPCM) is the mandatory wideband speech codec in the new generation digital enhanced cordless telephony (NG-DECT). Although in ADPCM the difference signal instead of the original signal is quantized and adaptive prediction is employed, redundancy is yet observed within the quantized samples. In this paper we apply a soft-decision speech decoding technique which exploits this redundancy in terms of a priori knowledge and the channel reliability information to NG-DECT.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views- Read more about Sparse Reconstruction of Quantized Speech Signals
- Log in to post comments
We propose sparse reconstruction techniques to improve the quality and / or reduce the bit-rate of standard speech coders. To that end, we assume signal sparsity in some transform domain and formulate the problem of reconstructing the original signal in terms of constrained l1-norm minimization. We use modern primal-dual methods in order to solve the resulting non-smooth convex optimization problem. Experiments show that with the proposed sparse reconstruction method the instrumentally predicted speech quality can be largely improved.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views- Read more about On the influence of quantization on the identifiability of emotions from voice coding parameters
- Log in to post comments
Although emotions play a major role in voice communication, the quality of their reproduction by low bit rate voice coders has never been investigated so far. This paper shows that the emotional state of a speaker can be identified automatically, with reasonable precision and accuracy, using conventional voice coding parameters (pitch, voicing, energy and LPC coefficients). It also shows that the performance of this identification degrades when these parameters are quantized, especially at lower rates (1200 bits/s).
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views- Read more about Adaptive selection of lag-window shape for linear predictive analysis in the 3GPP EVS codec
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views- Read more about Perceptual Long-Term Harmonic plus Noise Modeling for Speech Data Compression
- Log in to post comments
The harmonic plus noise model (HNM) is widely used for the modeling of audio signals. In this paper, we introduce perceptual frequency masking to the 2-band HNM, developed by Stylianou et al., applied to speech signals. An auditory model is used to recognize inaudible sinusoids, which will be removed from the set of model’s parameters in order to reduce the data size for speech coding.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views- Read more about Perceptual Long-Term Harmonic plus Noise Modeling for Speech Data Compression
- Log in to post comments
The harmonic plus noise model (HNM) is widely used for the modeling of audio signals. In this paper, we introduce perceptual frequency masking to the 2-band HNM, developed by Stylianou et al., applied to speech signals. An auditory model is used to recognize inaudible sinusoids, which will be removed from the set of model’s parameters in order to reduce the data size for speech coding.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views- Read more about Super-Wideband Fine Spectrum Quantization for Low-rate High-Quality MDCT Coding Mode of The 3GPP EVS Codec
- Log in to post comments
This article presents a low bit-rate super wideband MDCT coder, which is adopted as a part of the recently standardized codec for Enhanced Voice Services. To maximize codec performance at 13.2 kbps, existing algorithms are reviewed and several new tools are introduced into the low bit-rate MDCT coder to improve the performance of the coder while coding music and mixed content. A subjective listening test demonstrates the advantage of the proposed system for 13.2 kbps when compared to AMR-WB+.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
This presentation describes the bandwidth extension (BWE) method developed for the AMR-WB interoperable (AMR-WB IO) modes of the 3GPP EVS codec. The low-band signal (0-6.4 kHz) is coded using an enhanced version of ACELP as in AMR-WB and post-processed; the high-band (above 6.4 kHz) in contrast to AMR-WB is represented with a new BWE method. The decoded low-band excitation is adaptively extended to high frequencies and filtered in the DCT domain. The extended excitation is scaled by subframe gains and shaped by a weighted LPC synthesis filter.
- Categories:
 202 Views
202 Views