
- Read more about FOLLOWING THE EMBEDDING: IDENTIFYING TRANSITION PHENOMENA IN WAV2VEC 2.0 REPRESENTATIONS OF SPEECH AUDIO
- Log in to post comments
Although transformer-based models have improved the state-of-the-art in speech recognition, it is still not well understood what information from the speech signal these models encode in their latent representations. This study investigates the potential of using labelled data (TIMIT) to probe wav2vec 2.0 embeddings for insights into the encoding and visualisation of speech signal information at phone boundaries. Our experiment involves training probing models to detect phone-specific articulatory features in the hidden layers based on IPA classifications.
- Categories:
 96 Views
96 Views
- Read more about Detecting Check-Worthy Claims in Political Debates, Speeches, and Interviews Using Audio Data - Poster
- Log in to post comments
Developing tools to automatically detect check-worthy claims in political debates and speeches can greatly help moderators of debates, journalists, and fact-checkers. While previous work on this problem has focused exclusively on the text modality, here we explore the utility of the audio modality as an additional input. We create a new multimodal dataset (text and audio in English) containing 48 hours of speech from past political debates in the USA.
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views
- Read more about Detecting Check-Worthy Claims in Political Debates, Speeches, and Interviews Using Audio Data - Presentation
- Log in to post comments
Developing tools to automatically detect check-worthy claims in political debates and speeches can greatly help moderators of debates, journalists, and fact-checkers. While previous work on this problem has focused exclusively on the text modality, here we explore the utility of the audio modality as an additional input. We create a new multimodal dataset (text and audio in English) containing 48 hours of speech from past political debates in the USA.
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views
- Read more about [Poster] Selective Acoustic Feature Enhancement for Speech Emotion Recognition with Noisy Speech
- Log in to post comments
A speech emotion recognition (SER) system deployed on a real-world application can encounter speech contaminated with unconstrained background noise. To deal with this issue,
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views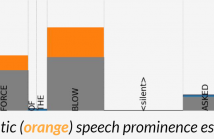
- Read more about [Poster] Crowdsourced and Automatic Speech Prominence Estimation
- Log in to post comments
The prominence of a spoken word is the degree to which an average native listener perceives the word as salient or emphasized relative to its context. Speech prominence estimation is the process of assigning a numeric value to the prominence of each word in an utterance. These prominence labels are useful for linguistic analysis, as well as training automated systems to perform emphasis-controlled text-to-speech or emotion recognition. Manually annotating prominence is time-consuming and expensive, which motivates the development of automated methods for speech prominence estimation.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about [Paper] Crowdsourced and Automatic Speech Prominence Estimation
- Log in to post comments
The prominence of a spoken word is the degree to which an average native listener perceives the word as salient or emphasized relative to its context. Speech prominence estimation is the process of assigning a numeric value to the prominence of each word in an utterance. These prominence labels are useful for linguistic analysis, as well as training automated systems to perform emphasis-controlled text-to-speech or emotion recognition. Manually annotating prominence is time-consuming and expensive, which motivates the development of automated methods for speech prominence estimation.
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views
- Read more about ASSD: Synthetic Speech Detection in the AAC Compressed Domain
- Log in to post comments
Synthetic human speech signals have become very easy to generate given modern text-to-speech methods. When these signals are shared on social media they are often compressed using the Advanced Audio Coding (AAC) standard. Our goal is to study if a small set of coding metadata contained in the AAC compressed bit stream is sufficient to detect synthetic speech. This would avoid decompressing of the speech signals before analysis. We call our proposed method AAC Synthetic Speech Detection (ASSD).
- Categories:
 38 Views
38 Views
- Read more about SPEECH-BASED EMOTION RECOGNITION WITH SELF-SUPERVISED MODELS USING ATTENTIVE CHANNEL-WISE CORRELATIONS AND LABEL SMOOTHING
- Log in to post comments
When recognizing emotions from speech, we encounter two common problems: how to optimally capture emotion-relevant information from the speech signal and how to best quantify or categorize the noisy subjective emotion labels. Self-supervised pre-trained representations can robustly capture information from speech enabling state-of-the-art results in many downstream tasks including emotion recognition. However, better ways of aggregating the information across time need to be considered as the relevant emotion information is likely to appear piecewise and not uniformly across the signal.
- Categories:
 52 Views
52 Views
- Read more about Federated Intelligent Terminals Facilitate Stuttering Monitoring
- Log in to post comments
Stuttering is a complicated language disorder. The most common form of stuttering is developmental stuttering, which begins in childhood. Early monitoring and intervention are essential for the treatment of children with stuttering. Automatic speech recognition technology has shown its great potential for non-fluent disorder identification, whereas the previous work has not considered the privacy of users' data. To this end, we propose federated intelligent terminals for automatic monitoring of stuttering speech in different contexts.
- Categories:
 89 Views
89 Views
End-to-End Spoken Language Understanding models are generally evaluated according to their overall accuracy, or separately on (a priori defined) data subgroups of interest.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views