
- Read more about SPATIAL ACTIVE NOISE CONTROL BASED ON INDIVIDUAL KERNEL INTERPOLATION OF PRIMARY AND SECONDARY SOUND FIELDS
- Log in to post comments
A spatial active noise control (ANC) method based on the individual kernel interpolation of primary and secondary sound fields is pro- posed. Spatial ANC is aimed at cancelling unwanted primary noise within a continuous region by using multiple secondary sources and microphones. A method based on the kernel interpolation of a sound field makes it possible to attenuate noise over the target region with flexible array geometry. Furthermore, by using the kernel function with directional weighting, prior information on primary noise source directions can be taken into consideration.
- Categories:
 101 Views
101 Views
- Read more about SPATIAL ACTIVE NOISE CONTROL BASED ON KERNEL INTERPOLATION WITH DIRECTIONAL WEIGHTING
- Log in to post comments
A spatial active noise control (ANC) method taking prior information on the approximate direction of primary noise sources into consideration is proposed. ANC aims to cancel incoming primary noise using secondary loudspeakers. Conventional multipoint ANC does not guarantee the reduction of noise between multiple discrete control points; therefore, several attempts have been made to reduce the noise over an entire target region, i.e., by spatial ANC.
- Categories:
 95 Views
95 Views
- Read more about Active Control of Line Spectral Noise with Simultaneous Secondary Path Modeling Without Auxiliary Noise
- Log in to post comments
Online secondary path modeling is appealing for most active noise control systems due to its benefit of effective tracking of the varying acoustic environment and possible variation of the control sources and sensors. However, the usually utilized additive noise method inevitably leads to the increase of residual noise. Recently we have found that it is possible to model the secondary path without any auxiliary noise as long as the noise to be controlled is not of line spectral property.
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views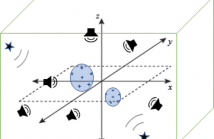
- Read more about Active noise control over multiple regions: performance analysis
- Log in to post comments
Active noise control (ANC) over space is a well-researched topic where multi-microphone, multi-loudspeaker systems are designed to minimize the noise over a spatial region of interest. In this paper, we perform an initial study on the more complex problem of simultaneous noise control over multiple target regions using a single ANC system. In particular, we investigate the maximum active noise control performance over the multiple target regions, given a particular setup of secondary loudspeakers.
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 Views
- Read more about Primary Path Estimator based on Individual Secondary Path for ANC Headphones
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 79 Views
79 Views
- Read more about Poster - Acoustic Equalization for Headphones Using a Fixed Feed-Forward Filter
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views
- Read more about Feedforward Spatial Active Noise Control Based on Kernel Interpolation of Sound Field
- Log in to post comments
A method for feedforward active noise control (ANC) over a spatial region is proposed. Conventional multipoint ANC aims to reduce the noise at multiple discrete positions; therefore, the noise reduction in the region between these points cannot be guaranteed. Recent studies revealed the possibility of spatial ANC, i.e., noise control in a continuous target region.
- Categories:
 58 Views
58 Views
- Read more about Global and Local Mode-domain Adaptive Algorithms for Spatial Active Noise Control Using Higher-order Sources
- Log in to post comments
The aim of spatial active noise control (ANC) is to attenuate noise over a certain space. Although a large-scale system is required to
achieve spatial ANC, mode-domain signal processing makes it possible to reduce the computational cost and improve the performance.
A higher-order source (HOS) has an advantage in sound field control due to its controllable directivity patterns. An array of HOS
can suppress an undesired exterior sound propagation while occupying a smaller physical space than a conventional omnidirectional
- Categories:
 60 Views
60 Views