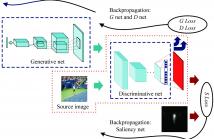
In this paper, we propose an accurate generative adversarial networks based saliency prediction model. Saliency network is an intact model to produce saliency maps. With the help of adversarial networks, feature extraction is more smooth and thorough. Moreover, the fully convolutional networks in saliency network facilitate the continuity and accuracy of pixel values in a saliency map. Compared with the six stateof-the-art methods, the proposed model has achieved highest accuracy. Besides, the performance of our model indicates that adversarial networks could be applied to more than classification. For future work, we will extend the algorithm to semi-supervised saliency prediction since DCGAN is a strong candidate for unsupervised learning.
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views- Read more about EFFECT OF WAVELET AND HYBRID CLASSIFICATION ON ACTION RECOGNITION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 3 Views
3 Views- Read more about ICIP_1343
- Log in to post comments
One of the most critical missions of sonar is to capture deep-sea pictures to depict sea floor and various objects, and provide an immense understanding of biology and geology in deep sea. Due to the poor condition of underwater acoustic channel, the captured sonar images very possibly suffer from several typical types of distortions before finally reaching to users. Unfortunately, very limited efforts have been devoted to collecting meaningful sonar image databases and benchmark reliable objective quality predictors.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views
- Read more about CONTRAST-ACCUMULATED HISTOGRAM EQUALIZATION FOR IMAGE ENHANCEMENT
- Log in to post comments
Among image enhancement methods, histogram equalization (HE) has received the most attention because of its intuitive implementation quality, high efficiency, and the monotonicity of its intensity mapping function. However, HE is indiscriminate and overemphasizes the contrast around intensities with large pixel populations but little visual importance. To address this issue, we propose an HE-based method that adaptively controls the contrast gain according to the potential visual importance of intensities and pixels.
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views- Read more about IMAGE GUIDED DEPTH ENHANCEMENT VIA DEEP FUSION AND LOCAL LINEAR REGULARIZATION
- Log in to post comments
Depth maps captured by RGB-D cameras are often noisy and incomplete at edge regions. Most existing methods assume that there is a co-occurrence of edges in depth map and its corresponding color image, and improve the quality of depth map guided by the color image. However, when the color image is noisy or richly detailed, the high frequency artifacts will be introduced into depth map. In this paper, we propose a deep residual network based on deep fusion and local linear regularization for guided depth enhancement.
- Categories:
 38 Views
38 Views
Visual context has formed a robust stimulation for visual perception. Spatio-temporal context in existing trackers sometimes shows weak reliability in visible light videos with poor quality. Supplemented by the infrared perception, this work exploits the role of visual context in tracking in a spatial-sequential-spectral view, by which to excavate dominance of different contexts in various scenarios.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about A SEMI-GLOBAL MOTION ESTIMATION OF A REPETITION PATTERN REGION FOR FRAME INTERPOLATION
- Log in to post comments
In motion compensated frame interpolation, a repetition
pattern in an image makes it difficult to derive an accurate
motion vector because multiple similar local minima exist in
the search space of the matching cost for motion estimation.
In order to improve the accuracy of motion estimation in a
repetition region, this paper attempts a semi-global approach
that exploits both local and global characteristics of a
repetition region. Experimental results demonstrate that the
proposed method significantly outperforms the previous local
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about SALIENCY DETECTION VIA LOCAL SINGLE GAUSSIAN MODEL
- Log in to post comments
ICIP 1195.pdf
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views- Read more about View synthesis with hierarchical clustering based occlusion filling
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views