- Read more about Street-to-Shop Shoe Retrieval with Multi-Scale Viewpoint Invariant Triplet Network
- Log in to post comments
In this paper we aim to find exactly the same shoes given a daily shoe photo (street scenario) that matches the online shop shoe photo (shop scenario). There are large visual differences between the street and shop scenario shoe images. To handle the discrepancy of different scenarios, we learn a feature embedding for shoes via a viewpoint-invariant triplet network, the feature activations of which reflect the inherent similarity between any two shoe images.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views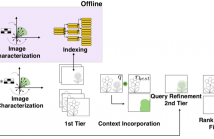
- Read more about Provenance Filtering for Multimedia Phylogeny
- Log in to post comments
Departing from traditional digital forensics modeling, which seeks to analyze single objects in isolation, multimedia phylogeny analyzes the evolutionary processes that influence digital objects and collections over time. One of its integral pieces is provenance filtering, which consists of searching a potentially large pool of objects for the most related ones with respect to a given query, in terms of possible ancestors (donors or contributors) and descendants.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views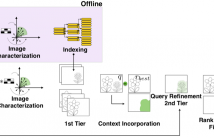
- Read more about PROVENANCE FILTERING FOR MULTIMEDIA PHYLOGENY
- Log in to post comments
Departing from traditional digital forensics modeling, which seeks to analyze single objects in isolation, multimedia phylogeny analyzes the evolutionary processes that influence digital objects and collections over time. One of its integral pieces is provenance filtering, which consists of searching a potentially large pool of objects for the most related ones with respect to a given query, in terms of possible ancestors (donors or contributors) and descendants.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views- Read more about Unsupervised Deep Hashing with Stacked Convolutional Autoencoders
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about PERSON RE-IDENTIFICATION USING VISUAL ATTENTION
- Log in to post comments
Despite recent attempts for solving the person re-identification problem, it remains a challenging task since a person’s appearance can vary significantly when large variations in view angle, human pose and illumination are involved. The concept of attention is one of the most interesting recent architectural innovations in neural networks. Inspired by that, in this paper we propose a novel approach based on using a gradient-based attention mechanism in deep convolution neural network for solving the person re-identification problem.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views- Read more about LEARNING SUPERVISED BINARY HASHING: OPTIMIZATION VS DIVERSITY
- Log in to post comments
Binary hashing is a practical approach for fast, approximate retrieval in large image databases. The goal is to learn a hash function that maps images onto a binary vector such that Hamming distances approximate semantic similarities. The search is then fast by using hardware support for binary operations. Most hashing papers define a complicated objective function that couples the single-bit hash functions.
- Categories:
 3 Views
3 ViewsWe introduce a novel approach to improve unsupervised hashing. Specifically, we propose a very efficient embedding method: Gaussian Mixture Model embedding (Gemb). The proposed method, using Gaussian Mixture Model, embeds feature vector into a low-dimensional vector and, simultaneously, enhances the discriminative property of features before passing them into hashing. Our experiment shows that the proposed method boosts the hashing performance of many state-of-the-art, e.g.
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 ViewsWe introduce a novel approach to improve unsupervised hashing. Specifically, we propose a very efficient embedding method: Gaussian Mixture Model embedding (Gemb). The proposed method, using Gaussian Mixture Model, embeds feature vector into a low-dimensional vector and, simultaneously, enhances the discriminative property of features before passing them into hashing. Our experiment shows that the proposed method boosts the hashing performance of many state-of-the-art, e.g.
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views
- Read more about LABEL CONSISTENT MATRIX FACTORIZATION BASED HASHING FOR CROSS-MODAL RETRIEVAL
- Log in to post comments
Matrix factorization based hashing has been very effective in addressing the cross-modal retrieval task. In this work, we propose a novel supervised hashing approach utilizing the concepts of matrix factorization which can seamlessly incorporate the label information. In the proposed approach, the latent factors for each individual modality are generated, which are then converted to the more discriminative label space using modality specific linear transformations.
- Categories:
 87 Views
87 Views